Dietary folate deficiency blocks prostate cancer progression in the TRAMP model
- PMID: 21836022
- PMCID: PMC3208799
- DOI: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-11-0140
Dietary folate deficiency blocks prostate cancer progression in the TRAMP model
Abstract
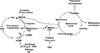
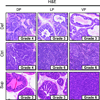
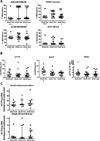
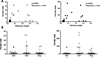
Dietary folate is essential in all tissues to maintain several metabolite pools and cellular proliferation. Prostate cells, due to specific metabolic characteristics, have increased folate demand to support proliferation and prevent genetic and epigenetic damage. Although several studies have found that dietary folate interventions can affect colon cancer biology in rodent models, its impact on prostate is unknown. The purpose of this study was to determine whether dietary folate manipulation, possibly being of primary importance for prostate epithelial cell metabolism, could significantly affect prostate cancer progression. Strikingly, mild dietary folate depletion arrested prostate cancer progression in 25 of 26 transgenic adenoma of the mouse prostate (TRAMP) mice, in which tumorigenesis is prostate-specific and characteristically aggressive. The significant effect on prostate cancer growth was characterized by size, grade, proliferation, and apoptosis analyses. Folate supplementation had a mild, nonsignificant, beneficial effect on grade. In addition, characterization of folate pools (correlated with serum), metabolite pools (polyamines and nucleotides), genetic and epigenetic damage, and expression of key biosynthetic enzymes in prostate tissue revealed interesting correlations with tumor progression. These findings indicate that prostate cancer is highly sensitive to folate manipulation and suggest that antifolates, paired with current therapeutic strategies, might significantly improve treatment of prostate cancer, the most commonly diagnosed cancer in American men.
Figures


References
-
- Gangjee A, Jain HD, Kurup S. Recent advances in classical and non-classical antifolates as antitumor and antiopportunistic infection agents: part I. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2007 Sep;7(5):524–542. - PubMed
-
- Gerner EW, Meyskens FL., Jr Polyamines and cancer: old molecules, new understanding. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004 Oct;4(10):781–792. - PubMed
-
- Loenen WA. S-adenosylmethionine: jack of all trades and master of everything? Biochem Soc Trans. 2006 Apr;34(Pt 2):330–333. - PubMed
-
- Cole BF, Baron JA, Sandler RS, Haile RW, Ahnen DJ, Bresalier RS, McKeown-Eyssen G, Summers RW, Rothstein RI, Burke CA, Snover DC, Church TR, Allen JI, Robertson DJ, Beck GJ, Bond JH, Byers T, Mandel JS, Mott LA, Pearson LH, Barry EL, Rees JR, Marcon N, Saibil F, Ueland PM, Greenberg ER. Folic acid for the prevention of colorectal adenomas: a randomized clinical trial. Jama. 2007 Jun 6;297(21):2351–2359. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

