Small-molecule activators of TMEM16A, a calcium-activated chloride channel, stimulate epithelial chloride secretion and intestinal contraction
- PMID: 21836025
- PMCID: PMC3205834
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.11-191627
Small-molecule activators of TMEM16A, a calcium-activated chloride channel, stimulate epithelial chloride secretion and intestinal contraction
Abstract
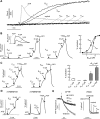
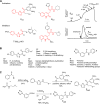
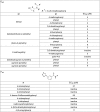
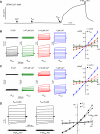
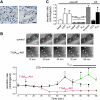
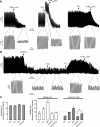
TMEM16A (ANO1) is a calcium-activated chloride channel (CaCC) expressed in secretory epithelia, smooth muscle, and other tissues. Cell-based functional screening of ∼110,000 compounds revealed compounds that activated TMEM16A CaCC conductance without increasing cytoplasmic Ca(2+). By patch-clamp, N-aroylaminothiazole "activators" (E(act)) strongly increased Cl(-) current at 0 Ca(2+), whereas tetrazolylbenzamide "potentiators" (F(act)) were not active at 0 Ca(2+) but reduced the EC(50) for Ca(2+)-dependent TMEM16A activation. Of 682 analogs tested, the most potent activator (E(act)) and potentiator (F(act)) produced large and more sustained CaCC Cl(-) currents than general agonists of Ca(2+) signaling, with EC(50) 3-6 μM and Cl(-) conductance comparable to that induced transiently by Ca(2+)-elevating purinergic agonists. Analogs of activators were identified that fully inhibited TMEM16A Cl(-) conductance, providing further evidence for direct TMEM16A binding. The TMEM16A activators increased CaCC conductance in human salivary and airway submucosal gland epithelial cells, and IL-4 treated bronchial cells, and stimulated submucosal gland secretion in human bronchi and smooth muscle contraction in mouse intestine. Small-molecule, TMEM16A-targeted activators may be useful for drug therapy of cystic fibrosis, dry mouth, and gastrointestinal hypomotility disorders, and for pharmacological dissection of TMEM16A function.
Figures

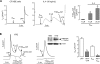
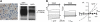
References
-
- Hartzell C., Putzier I., Arreola J. (2005) Calcium-activated chloride channels. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 67, 719–758 - PubMed
-
- Eggermont J. (2004) Calcium-activated chloride channels: (un) known, (un)loved? Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 1, 22–27 - PubMed
-
- Yang Y. D., Cho H., Koo J. Y., Tak M. H., Cho Y., Shim W. S., Park S. P., Lee J., Lee B., Kim B. M., Raouf R., Shin Y. K., Oh U. (2008) TMEM16A confers receptor-activated calcium-dependent chloride conductance. Nature 455, 1210–1215 - PubMed
-
- Caputo A., Caci E., Ferrera L., Pedemonte N., Barsanti C., Sondo E., Pfeffer U., Ravazzolo R., Zegarra-Moran O., Galietta L. J. (2008) TMEM16A, a membrane protein associated with calcium-dependent chloride channel activity. Science 322, 590–594 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL73856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY013574/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- DK86125/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB000415/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK035124/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK72517/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- EY13574/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- DK35124/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL073856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK072517/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 DK086125/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- EB00415/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK035124/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 EB000415/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

