C1q/TNF-related proteins, a family of novel adipokines, induce vascular relaxation through the adiponectin receptor-1/AMPK/eNOS/nitric oxide signaling pathway
- PMID: 21836066
- PMCID: PMC3197867
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.231050
C1q/TNF-related proteins, a family of novel adipokines, induce vascular relaxation through the adiponectin receptor-1/AMPK/eNOS/nitric oxide signaling pathway
Abstract
Objective: Reduced plasma adiponectin (APN) in diabetic patients is associated with endothelial dysfunction. However, APN knockout animals manifest modest systemic dysfunction unless metabolically challenged. The protein family CTRPs (C1q/TNF-related proteins) has recently been identified as APN paralogs and some CTRP members share APN's metabolic regulatory function. However, the vasoactive properties of CTRPs remain completely unknown.
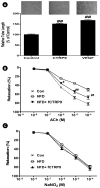
Methods and results: The vasoactivity of currently identified murine CTRP members was assessed in aortic vascular rings and underlying molecular mechanisms was elucidated in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Of 8 CTRPs, CTRPs 3, 5, and 9 caused significant vasorelaxation. The vasoactive potency of CTRP9 exceeded that of APN (3-fold) and is endothelium-dependent and nitric oxide (NO)-mediated. Mechanistically, CTRP9 increased AMPK/Akt/eNOS phosphorylation and increased NO production. AMPK knockdown completely blocked CTRP9-induced Akt/eNOS phosphorylation and NO production. Akt knockdown had no significant effect on CTRP9-induced AMPK phosphorylation, but blocked eNOS phosphorylation and NO production. Adiponectin receptor 1, but not receptor 2, knockdown blocked CTRP9-induced AMPK/Akt/eNOS phosphorylation and NO production. Finally, preincubating vascular rings with an AMPK-inhibitor abolished CTRP9-induced vasorelaxative effects.
Conclusion: We have provided the first evidence that CTRP9 is a novel vasorelaxative adipocytokine that may exert vasculoprotective effects via the adiponectin receptor 1/AMPK/eNOS dependent/NO mediated signaling pathway.
Figures





References
-
- Diamant M, Tushuizen ME. The metabolic syndrome and endothelial dysfunction: common highway to type 2 diabetes and CVD. Curr Diab Rep. 2006;6:279–286. - PubMed
-
- Kim JA, Montagnani M, Koh KK, Quon MJ. Reciprocal relationships between insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction: molecular and pathophysiological mechanisms. Circulation. 2006;113:1888–1904. - PubMed
-
- Quinones MJ, Nicholas SB, Lyon CJ. Insulin resistance and the endothelium. Curr Diab Rep. 2005;5:246–253. - PubMed
-
- Shimabukuro M, Higa N, Asahi T, Oshiro Y, Takasu N, Tagawa T, Ueda S, Shimomura I, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y. Hypoadiponectinemia is closely linked to endothelial dysfunction in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:3236–3240. - PubMed
-
- Ouchi N, Ohishi M, Kihara S, Funahashi T, Nakamura T, Nagaretani H, Kumada M, Ohashi K, Okamoto Y, Nishizawa H, Kishida K, Maeda N, Nagasawa A, Kobayashi H, Hiraoka H, Komai N, Kaibe M, Rakugi H, Ogihara T, Matsuzawa Y. Association of hypoadiponectinemia with impaired vasoreactivity. Hypertension. 2003;42:231–234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

