A multisite assessment of the quantitative capabilities of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay
- PMID: 21836139
- PMCID: PMC3208646
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201103-0536OC
A multisite assessment of the quantitative capabilities of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay
Abstract
Rationale: The Xpert MTB/RIF is an automated molecular test for Mycobacterium tuberculosis that estimates bacterial burden by measuring the threshold-cycle (Ct) of its M. tuberculosis-specific real-time polymerase chain reaction. Bacterial burden is an important biomarker for disease severity, infection control risk, and response to therapy.
Objectives: Evaluate bacterial load quantitation by Xpert MTB/RIF compared with conventional quantitative methods.
Methods: Xpert MTB/RIF results were compared with smear-microscopy, semiquantiative solid culture, and time-to-detection in liquid culture for 741 patients and 2,008 samples tested in a multisite clinical trial. An internal control real-time polymerase chain reaction was evaluated for its ability to identify inaccurate quantitative Xpert MTB/RIF results.
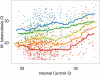
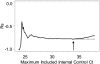
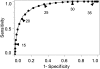
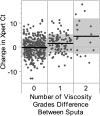
Measurements and main results: Assays with an internal control Ct greater than 34 were likely to be inaccurately quantitated; this represented 15% of M. tuberculosis-positive tests. Excluding these, decreasing M. tuberculosis Ct was associated with increasing smear microscopy grade for smears of concentrated sputum pellets (r(s) = -0.77) and directly from sputum (r(s) =-0.71). A Ct cutoff of approximately 27.7 best predicted smear-positive status. The association between M. tuberculosis Ct and time-to-detection in liquid culture (r(s) = 0.68) and semiquantitative colony counts (r(s) = -0.56) was weaker than smear. Tests of paired same-patient sputum showed that high viscosity sputum samples contained ×32 more M. tuberculosis than nonviscous samples. Comparisons between the grade of the acid-fast bacilli smear and Xpert MTB/RIF quantitative data across study sites enabled us to identify a site outlier in microscopy.
Conclusions: Xpert MTB/RIF quantitation offers a new, standardized approach to measuring bacterial burden in the sputum of patients with tuberculosis.
Figures


References
-
- Perrin FM, Woodward N, Phillips PP, McHugh TD, Nunn AJ, Lipman MC, Gillespie SH. Radiological cavitation, sputum mycobacterial load and treatment response in pulmonary tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2010;14:1596–1602 - PubMed
-
- Small PM, Pai M. Tuberculosis diagnosis—time for a game change. N Engl J Med 2010;363:1070–1071 - PubMed
-
- Multiple misdiagnoses of tuberculosis resulting from laboratory error—Wisconsin, 1996. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 1997;46:797–801 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

