Modeling the effects of drug binding on the dynamic instability of microtubules
- PMID: 21836336
- PMCID: PMC3168699
- DOI: 10.1088/1478-3975/8/5/056004
Modeling the effects of drug binding on the dynamic instability of microtubules
Abstract
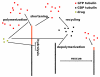
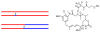
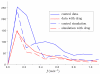
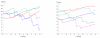
We propose a stochastic model that accounts for the growth, catastrophe and rescue processes of steady-state microtubules assembled from MAP-free tubulin in the possible presence of a microtubule-associated drug. As an example of the latter, we both experimentally and theoretically study the perturbation of microtubule dynamic instability by S-methyl-D-DM1, a synthetic derivative of the microtubule-targeted agent maytansine and a potential anticancer agent. Our model predicts that among the drugs that act locally at the microtubule tip, primary inhibition of the loss of GDP tubulin results in stronger damping of microtubule dynamics than inhibition of GTP tubulin addition. On the other hand, drugs whose action occurs in the interior of the microtubule need to be present in much higher concentrations to have visible effects.
Figures
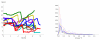

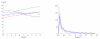

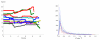
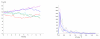

Similar articles
-
Maytansine and cellular metabolites of antibody-maytansinoid conjugates strongly suppress microtubule dynamics by binding to microtubules.Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 Oct;9(10):2689-99. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0644. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010. PMID: 20937594 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of microtubule elongation by GDP.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 29;137(1):351-8. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91217-9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986. PMID: 3718509
-
Maytansine inhibits nucleotide binding at the exchangeable site of tubulin.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 16;128(3):1239-46. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91073-3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985. PMID: 4004859
-
Guanosine-5'-triphosphate hydrolysis and tubulin polymerization. Review article.Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Sep 3;47(2):97-113. doi: 10.1007/BF00234410. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982. PMID: 6755216 Review.
-
Microtubule dynamics.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;4(1):58-65. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90059-l. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992. PMID: 1558755 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of mitotic arrest induced by dolastatin 15 involves loss of tension across kinetochore pairs.Mol Cell Biochem. 2013 Oct;382(1-2):93-102. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1721-8. Epub 2013 Jun 7. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23744533
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
