Propolis prevents hepatorenal injury induced by chronic exposure to carbon tetrachloride
- PMID: 21837248
- PMCID: PMC3151521
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/235358
Propolis prevents hepatorenal injury induced by chronic exposure to carbon tetrachloride
Abstract
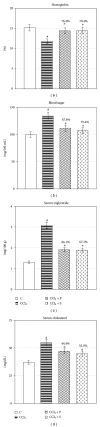
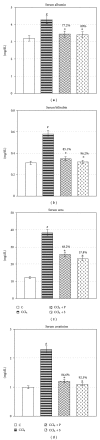
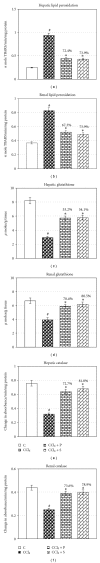
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl(4)) is a well-known hepatotoxicant, and its exposure induces hepatorenal injury via oxidative stress and biochemical alterations. This study had been conducted to confirm the protective role of propolis extract on CCl(4)-induced hepatorenal oxidative stress and resultant injury. Propolis extracts collected from Gwalior district and 24 female Sprague Dawley rats were used for experiment. Animals were exposed to CCl(4) (0.15 mL/kg, i.p.) for 12 weeks (5 days/week) followed by treatment with propolis extract (200 mg/kg, p.o.) for consecutive 2 weeks. CCl(4) exposure significantly depleted blood sugar and hemoglobin level and raised the level of transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, lactate dehydrogenase, protein, urea, albumin, bilirubin, creatinine, triglycerides, and cholesterol in serum. Lipid peroxidation was enhanced, whereas GSH was decreased significantly in liver and kidney in CCl(4)-intoxicated group. Ethanolic extract of propolis successfully prevented these alterations in experimental animals. Activities of catalase, adenosine triphosphatase, glucose-6-phosphatase, acid, and alkaline phosphatase were also maintained towards normal with propolis therapy. Light microscopical studies showed considerable protection in liver and kidney with propolis treatment, thus, substantiated biochemical observations. This study confirmed hepatoprotective potential of propolis extract against chronic injury induced by CCl(4) by regulating antioxidative defense activities.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Propolis reverses acetaminophen induced acute hepatorenal alterations: a biochemical and histopathological approach.Arch Pharm Res. 2008 Apr;31(4):451-61. doi: 10.1007/s12272-001-1178-5. Epub 2008 May 1. Arch Pharm Res. 2008. PMID: 18449502
-
Multiple treatment of propolis extract ameliorates carbon tetrachloride induced liver injury in rats.Food Chem Toxicol. 2008 Aug;46(8):2703-12. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2008.04.025. Epub 2008 Apr 27. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18572298
-
Duration-dependent hepatoprotective effects of propolis extract against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver damage in rats.Adv Ther. 2007 Sep-Oct;24(5):1136-45. doi: 10.1007/BF02877719. Adv Ther. 2007. PMID: 18029340
-
Reversal of acetaminophen induced subchronic hepatorenal injury by propolis extract in rats.Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2009 Jan;27(1):17-25. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2008.07.003. Epub 2008 Jul 18. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 21791392
-
Propolis protects CYP 2E1 enzymatic activity and oxidative stress induced by carbon tetrachloride.Mol Cell Biochem. 2007 Aug;302(1-2):215-24. doi: 10.1007/s11010-007-9443-4. Epub 2007 Apr 5. Mol Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17410408
Cited by
-
Defensive impact of propolis against CCl4 actuated rats' testicular damage.J Adv Vet Anim Res. 2021 Mar 5;8(1):70-77. doi: 10.5455/javar.2021.h487. eCollection 2021 Mar. J Adv Vet Anim Res. 2021. PMID: 33860015 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective effects of Berberis vulgaris L. extract/β cyclodextrin on carbon tetrachloride-induced acute toxicity in mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(7):9014-9034. doi: 10.3390/ijms13079014. Epub 2012 Jul 19. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22942749 Free PMC article.
-
Propolis in Metabolic Syndrome and Its Associated Chronic Diseases: A Narrative Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Feb 26;10(3):348. doi: 10.3390/antiox10030348. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33652692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Flavonoids from Propolis via Nrf2 and NF-κB Pathways.Foods. 2022 Aug 13;11(16):2439. doi: 10.3390/foods11162439. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36010439 Free PMC article.
-
The protective role of antioxidants in the defence against ROS/RNS-mediated environmental pollution.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:671539. doi: 10.1155/2014/671539. Epub 2014 Jul 20. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014. PMID: 25140198 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lima CF, Fernandes-Ferreira M, Pereira-Wilson C. Drinking of Salvia officinalis tea increases CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2007;45(3):456–464. - PubMed
-
- Loguercio C, Federico A. Oxidative stress in viral and alcoholic hepatitis. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2003;34(1):1–10. - PubMed
-
- Vitaglione P, Morisco F, Caporaso N, Fogliano V. Dietary antioxidant compounds and liver health. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 2004;44(7-8):575–586. - PubMed
-
- Jaeschke H, Gores GJ, Cederbaum AI, Hinson JA, Pessayre D, Lemasters JJ. Mechanisms of hepatotoxicity. Toxicological Sciences. 2002;65(2):166–176. - PubMed
-
- Tasduq SA, Kaiser P, Gupta DK, et al. Protective effect of a 50% hydroalcoholic fruit extract of Emblica officinalis against anti-tuberculosis drugs induced liver toxicity. Phytotherapy Research. 2005;19(3):193–197. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

