Endothelial targeting of antibody-decorated polymeric filomicelles
- PMID: 21838300
- PMCID: PMC3342815
- DOI: 10.1021/nn2015453
Endothelial targeting of antibody-decorated polymeric filomicelles
Abstract
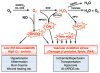
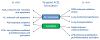
The endothelial lining of the lumen of blood vessels is a key therapeutic target for many human diseases. Polymeric filomicelles that self-assemble from polyethylene oxide (PEO)-based diblock copolymers are long and flexible rather than small or rigid, can be loaded with drugs, and--most importantly--they circulate for a prolonged period of time in the bloodstream due in part to flow alignment. Filomicelles seem promising for targeted drug delivery to endothelial cells because they can in principle adhere strongly, length-wise to specific cell surface determinants. In order to achieve such a goal of vascular drug delivery, two fundamental questions needed to be addressed: (i) whether these supramolecular filomicelles retain structural integrity and dynamic flexibility after attachment of targeting molecules such as antibodies, and (ii) whether the avidity of antibody-carrying filomicelles is sufficient to anchor the carrier to the endothelial surface despite the effects of flow that oppose adhesive interactions. Here we make targeted filomicelles that bear antibodies which recognize distinct endothelial surface molecules. We characterize these antibody targeted filomicelles and prove that (i) they retain structural integrity and dynamic flexibility and (ii) they adhere to endothelium with high specificity both in vitro and in vivo. These results provide the basis for a new drug delivery approach employing antibody-targeted filomicelles that circulate for a prolonged time yet bind to endothelial cells in vascular beds expressing select markers.
© 2011 American Chemical Society
Figures

References
-
- Thomas SR, Witting PK, Drummond GR. Redox control of endothelial function and dysfunction: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Anti-oxid Redox Signal. 2008;10(10):1713–1765. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka KA, Key NS, Levy JH. Blood coagulation: hemostasis and thrombin regulation. Anesth Analg. 2009;108(5):1433–1446. - PubMed
-
- Boffa MB, Koschinsky ML. Curiouser and curiouser: recent advances in measurement of thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI) and in understanding its molecular genetics, gene regulation, and biological roles. Clin Biochem. 2007;40(7):431–442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

