Evaluation of the effects of hospital visit stress on physiologic parameters in the cat
- PMID: 21839664
- PMCID: PMC10832771
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jfms.2011.07.003
Evaluation of the effects of hospital visit stress on physiologic parameters in the cat
Abstract
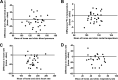
Physiologic parameters such as blood pressure, rectal temperature, heart rate, and respiratory rate are an important part of the medical assessment of a patient. However, these factors can potentially be affected by stress. The purpose of this study was to compare physiologic parameter data gathered from cats in the home environment with those gathered in a veterinary hospital. Thirty healthy cats were evaluated both at home and at Colorado State University's Veterinary Medical Center. Doppler systolic blood pressure, temperature, heart rate, and respiratory rate were recorded, and the differences between the values obtained in the home and veterinary clinic environments were evaluated using the Wilcoxon sign rank test. A significant difference was found in blood pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rate between the home and veterinary hospital environments. This information may help practitioners recognize that physiologic abnormalities can sometimes be due to transportation or environmental stress rather than medical illness.
Copyright © 2011 ISFM and AAFP. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Flood J. The diagnostic approach to fever of unknown origin in cats. Compend Contin Educ Vet 2009; 31: 26–31. - PubMed
-
- Kreisberg JI, Bulger RE, Trump BF, Nagle RB. Effects of transient hypotension on the structure and function of rat kidney. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol 1976; 22: 121–33. - PubMed
-
- Polzin DJ, Osborne CA, Ross SJ. Chronic kidney disease. In: Ettinger SJ, Feldman EC, eds. Textbook of veterinary internal medicine. 6th edn. St Louis, MO: WB Saunders, 2005. 1756–85.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

