Influence of C-terminal α-helix hydrophobicity and aromatic amino acid content on apolipoprotein A-I functionality
- PMID: 21840419
- PMCID: PMC3227795
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.07.020
Influence of C-terminal α-helix hydrophobicity and aromatic amino acid content on apolipoprotein A-I functionality
Abstract
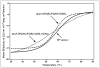
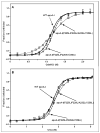
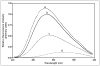
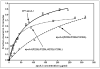
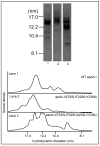
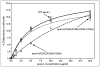
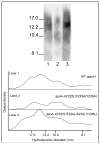
The apoA-I molecule adopts a two-domain tertiary structure and the properties of these domains modulate the ability to form HDL particles. Thus, human apoA-I differs from mouse apoA-I in that it can form smaller HDL particles; the C-terminal α-helix is important in this process and human apoA-I is unusual in containing aromatic amino acids in the non-polar face of this amphipathic α-helix. To understand the influence of these aromatic amino acids and the associated high hydrophobicity, apoA-I variants were engineered in which aliphatic amino acids were substituted with or without causing a decrease in overall hydrophobicity. The variants human apoA-I (F225L/F229A/Y236A) and apoA-I (F225L/F229L/A232L/Y236L) were compared to wild-type (WT) apoA-I for their abilities to (1) solubilize phospholipid vesicles and form HDL particles of different sizes, and (2) mediate cellular cholesterol efflux and create nascent HDL particles via ABCA1. The loss of aromatic residues and concomitant decrease in hydrophobicity in apoA-I (F225L/F229A/Y236A) has no effect on protein stability, but reduces by a factor of about three the catalytic efficiencies (V(max)/K(m)) of vesicle solubilization and cholesterol efflux; also, relatively large HDL particles are formed. With apoA-I (F225L/F229L/A232L/Y236L) where the hydrophobicity is restored by the presence of only leucine residues in the helix non-polar face, the catalytic efficiencies of vesicle solubilization and cholesterol efflux are similar to those of WT apoA-I; this variant forms smaller HDL particles. Overall, the results show that the hydrophobicity of the non-polar face of the C-terminal amphipathic α-helix plays a critical role in determining apoA-I functionality but aromatic amino acids are not required. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled Advances in High Density Lipoprotein Formation and Metabolism: A Tribute to John F. Oram (1945-2010).
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The roles of C-terminal helices of human apolipoprotein A-I in formation of high-density lipoprotein particles.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1841(1):80-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.10.005. Epub 2013 Oct 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24120703 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of apolipoprotein (Apo) A-I structure on nascent high density lipoprotein (HDL) particle size distribution.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 15;285(42):31965-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.126292. Epub 2010 Aug 2. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20679346 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of the C-terminal helix by single amino acid deletion is directly responsible for impaired cholesterol efflux ability of apolipoprotein A-I Nichinan.J Lipid Res. 2010 Apr;51(4):809-18. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M002113. Epub 2009 Oct 5. J Lipid Res. 2010. PMID: 19805625 Free PMC article.
-
High density lipoprotein structure-function and role in reverse cholesterol transport.Subcell Biochem. 2010;51:183-227. doi: 10.1007/978-90-481-8622-8_7. Subcell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20213545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Site-specific oxidation of apolipoprotein A-I impairs cholesterol export by ABCA1, a key cardioprotective function of HDL.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Mar;1821(3):490-501. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.11.011. Epub 2011 Dec 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22178192 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The roles of C-terminal helices of human apolipoprotein A-I in formation of high-density lipoprotein particles.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1841(1):80-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.10.005. Epub 2013 Oct 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24120703 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of apolipoprotein A-I with high-density lipoprotein particles.Biochemistry. 2013 Mar 19;52(11):1963-72. doi: 10.1021/bi400032y. Epub 2013 Mar 4. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23425306 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein a-I is a potential mediator of remote ischemic preconditioning.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 14;8(10):e77211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077211. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24155931 Free PMC article.
-
Is ABCA1 a lipid transfer protein?J Lipid Res. 2018 May;59(5):749-763. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R082313. Epub 2018 Jan 5. J Lipid Res. 2018. PMID: 29305383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of the C-terminal domain of human apolipoprotein A-I using a chimeric apolipoprotein.Protein Expr Purif. 2017 Sep;137:13-19. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2017.06.008. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Protein Expr Purif. 2017. PMID: 28624493 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

