Prenatal choline deficiency does not enhance hippocampal vulnerability after kainic acid-induced seizures in adulthood
- PMID: 21840511
- PMCID: PMC3166969
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.07.042
Prenatal choline deficiency does not enhance hippocampal vulnerability after kainic acid-induced seizures in adulthood
Abstract
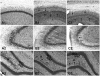
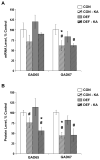
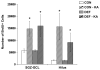
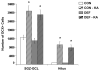
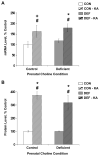
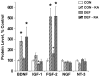
Choline is a vital nutrient needed during early development for both humans and rodents. Severe dietary choline deficiency during pregnancy leads to birth defects, while more limited deficiency during mid- to late pregnancy causes deficits in hippocampal plasticity in adult rodent offspring that are accompanied by cognitive deficits only when task demands are high. Because prenatal choline supplementation confers neuroprotection of the adult hippocampus against a variety of neural insults and aids memory, we hypothesized that prenatal choline deficiency may enhance vulnerability to neural injury. To examine this, adult offspring of rat dams either fed a control diet (CON) or one deficient in choline (DEF) during embryonic days 12-17 were given multiple injections (i.p.) of saline (control) or kainic acid to induce seizures and were euthanized 16 days later. Perhaps somewhat surprisingly, DEF rats were not more susceptible to seizure induction and showed similar levels of seizure-induced hippocampal histopathology, GAD expression loss, upregulated hippocampal GFAP and growth factor expression, and increased dentate cell and neuronal proliferation as that seen in CON rats. Although prenatal choline deficiency compromises adult hippocampal plasticity in the intact brain, it does not appear to exacerbate the neuropathological response to seizures in the adult hippocampus at least shortly after excitotoxic injury.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Water maze experience and prenatal choline supplementation differentially promote long-term hippocampal recovery from seizures in adulthood.Hippocampus. 2011 Jun;21(6):584-608. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20783. Epub 2010 Mar 15. Hippocampus. 2011. PMID: 20232399 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal choline deficiency increases choline transporter expression in the septum and hippocampus during postnatal development and in adulthood in rats.Brain Res. 2007 Jun 2;1151:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.03.004. Epub 2007 Mar 12. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17399691 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial memory and hippocampal plasticity are differentially sensitive to the availability of choline in adulthood as a function of choline supply in utero.Brain Res. 2008 Oct 27;1237:153-66. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.08.074. Epub 2008 Sep 4. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18778697 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal choline supplementation attenuates neuropathological response to status epilepticus in the adult rat hippocampus.Neurobiol Dis. 2008 May;30(2):255-69. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2008.01.008. Epub 2008 Feb 16. Neurobiol Dis. 2008. PMID: 18353663 Free PMC article.
-
Choline: critical role during fetal development and dietary requirements in adults.Annu Rev Nutr. 2006;26:229-50. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.26.061505.111156. Annu Rev Nutr. 2006. PMID: 16848706 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Systematic Review of the Dietary Choline Impact on Cognition from a Psychobiological Approach: Insights from Animal Studies.Nutrients. 2021 Jun 8;13(6):1966. doi: 10.3390/nu13061966. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34201092 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary choline levels modify the effects of prenatal alcohol exposure in rats.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2017 Jan-Feb;59:43-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2016.11.007. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2017. PMID: 27888055 Free PMC article.
-
In Up to My Ears and Temporal Lobes: Effects of Early Life Stress on Epilepsy Development.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2022;55:17-40. doi: 10.1007/7854_2020_190. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 33454921
References
-
- Albright CD, Tsai AY, Friedrich CB, Mar MH, Zeisel SH. Choline availability alters embryonic development of the hippocampus and septum in the rat. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1999;113:13–20. - PubMed
-
- Anderson MF, Aberg MA, Nilsson M, Eriksson PS. Insulin-like growth factor-I and neurogenesis in the adult mammalian brain. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2002;134:115–22. - PubMed
-
- Blusztajn JK, Cermak JM, Holler T, Jackson DA. Imprinting of hippocampal metabolism of choline by its availability during gestation: implications for cholinergic neurotransmission. J Physiol Paris. 1998;92:199–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

