Clinical complexity and the effectiveness of an intervention for depressed diabetes patients
- PMID: 21840915
- PMCID: PMC3983967
- DOI: 10.1177/1742395311409259
Clinical complexity and the effectiveness of an intervention for depressed diabetes patients
Abstract
Objectives: In a trial completed in 2010, US patients with diabetes and depression were randomized to usual care or telephone cognitive behavioural therapy that emphasized physical activity. Twelve-month intervention effects were observed for blood pressure, depression, and pedometer-measured step-counts. This study examined variation in intervention effects across patient subgroups defined by a measure of clinical complexity.
Methods: Three groups of patients were identified at baseline using the Vector Model of Complexity that recognizes socioeconomic, biological, behavioural, and other determinants of treatment response. Complexity-by-intervention interactions were examined using regression models.
Results: Intervention effects for blood pressure, depression, and step-counts differed across complexity levels (each p < 0.01). Effects on Beck Depression Inventory scores were greater in the low-complexity group (-8.8) than in the medium- (-3.2) or high-complexity groups (-2.7). Physical activity effects also were greatest in the low-complexity group (increase of 1498 steps per day). In contrast, systolic blood pressure effects were greater among intervention patients with high complexity (-8.5 mmHg).
Conclusions: This intervention had varying impacts on physical and mental health depending on patients' clinical complexity. Physical activity and depressive symptom gains may be more likely among less complex patients, although more complex patients may achieve cardiovascular benefits through decreased blood pressures.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01106885.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
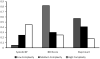
References
-
- Lustman PJ, Anderson RJ, Freedland KE, de Groot M, Carney RM, Clouse RE. Depression and poor glycemic control: a meta-analytic review of the literature. Diabetes Care. 2000;23(7):934–942. - PubMed
-
- Ciechanowski PS, Katon WJ, Russo JE. Depression and diabetes: impact of depressive symptoms on adherence, function, and costs. Arch Intern Med. 2000 Nov 27;160(21):3278–3285. - PubMed
-
- Subramaniam M, Sum CF, Pek E, et al. Comorbid depression and increased health care utilisation in individuals with diabetes. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2009 May-Jun;31(3):220–224. - PubMed
-
- de Groot M, Anderson R, Freedland KE, Clouse RE, Lustman PJ. Association of depression and diabetes complications: a meta-analysis. Psychosom Med. 2001 Jul-Aug;63(4):619–630. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

