15q11.2-13.3 chromatin analysis reveals epigenetic regulation of CHRNA7 with deficiencies in Rett and autism brain
- PMID: 21840925
- PMCID: PMC3196884
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddr357
15q11.2-13.3 chromatin analysis reveals epigenetic regulation of CHRNA7 with deficiencies in Rett and autism brain
Abstract
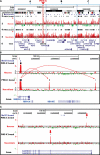
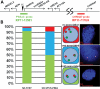
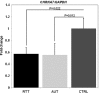
Copy number variations (CNVs) within human 15q11.2-13.3 show reduced penetrance and variable expressivity in a range of neurologic disorders. Therefore, characterizing 15q11.2-13.3 chromatin structure is important for understanding the regulation of this locus during normal neuronal development. Deletion of the Prader-Willi imprinting center (PWS-IC) within 15q11.2-13.3 disrupts long-range imprinted gene expression resulting in Prader-Willi syndrome. Previous results establish that MeCP2 binds to the PWS-IC and is required for optimal expression of distal GABRB3 and UBE3A. To examine the hypothesis that MeCP2 facilitates 15q11.2-13.3 transcription by linking the PWS-IC with distant elements, chromosome capture conformation on chip (4C) analysis was performed in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. SH-SY5Y neurons had 2.84-fold fewer 15q11.2-13.3 PWS-IC chromatin interactions than undifferentiated SH-SY5Y neuroblasts, revealing developmental chromatin de-condensation of the locus. Out of 68 PWS-IC interactions with15q11.2-13.3 identified by 4C analysis and 62 15q11.2-13.3 MeCP2-binding sites identified by previous ChIP-chip studies, only five sites showed overlap. Remarkably, two of these overlapping PWS-IC- and MeCP2-bound sites mapped to sites flanking CHRNA7 (cholinergic receptor nicotinic alpha 7) encoding the cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 7. PWS-IC interaction with CHRNA7 in neurons was independently confirmed by fluorescent in situ hybridization analysis. Subsequent quantitative transcriptional analyses of frontal cortex from Rett syndrome and autism patients revealed significantly reduced CHRNA7 expression compared with controls. Together, these results suggest that transcription of CHRNA7 is modulated by chromatin interactions with the PWS-IC. Thus, loss of long-range chromatin interactions within 15q11.2-13.3 may contribute to multiple human neurodevelopmental disorders.
Figures


References
-
- Buiting K., Lich C., Cottrell S., Barnicoat A., Horsthemke B. A 5-kb imprinting center deletion in a family with Angelman syndrome reduces the shortest region of deletion overlap to 880 bp. Hum. Genet. 1999;105:665–666. - PubMed
-
- Horsthemke B., Wagstaff J. Mechanisms of imprinting of the Prader–Willi/Angelman region. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2008;146A:2041–2052. - PubMed
-
- Peng X., Katz M., Gerzanich V., Anand R., Lindstrom J. Human alpha 7 acetylcholine receptor: cloning of the alpha 7 subunit from the SH-SY5Y cell line and determination of pharmacological properties of native receptors and functional alpha 7 homomers expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Mol. Pharmacol. 1994;45:546–554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

