Active role of the interdomain linker of AraC
- PMID: 21840981
- PMCID: PMC3187213
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.05339-11
Active role of the interdomain linker of AraC
Abstract
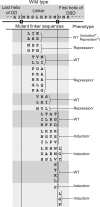
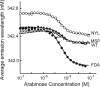
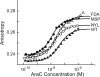
Mutations in the interdomain linker of the gene for the AraC regulatory protein of Escherichia coli that severely interfere with the protein's ability either to repress or to activate transcription have been found. These mutations have relatively small effects on the dimerization domain's ability to bind arabinose or to dimerize the protein or on the DNA-binding domain's affinity for a single DNA half-site. The linker mutations, however, dramatically change the affinity of AraC for binding to two direct-repeat DNA half-sites. Less dramatically, the induction-deficient linker variants also display altered DNA sequence selectivity. These results show that changing the sequence of the interdomain linker can profoundly affect the dimerization domain-DNA-binding domain interactions in AraC. The smaller effects on the functions of the individual domains could be the direct result of the linker alterations but more likely are the indirect result of the altered dimerization domain-DNA-binding domain interactions. In summary, the linker does not simply function as a passive and flexible connector between the domains of AraC but, instead, is more directly involved in the protein's dimerization domain-DNA-binding domain interactions.
Figures
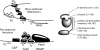

Similar articles
-
Arabinose Alters Both Local and Distal H-D Exchange Rates in the Escherichia coli AraC Transcriptional Regulator.Biochemistry. 2019 Jul 2;58(26):2875-2882. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00389. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 31199144 Free PMC article.
-
A genetic and physical study of the interdomain linker of E. Coli AraC protein--a trans-subunit communication pathway.Proteins. 2016 Apr;84(4):448-60. doi: 10.1002/prot.24990. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Proteins. 2016. PMID: 26800223
-
Helical Behavior of the Interdomain Linker of the Escherichia coli AraC Protein.Biochemistry. 2019 Jul 2;58(26):2867-2874. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00234. Epub 2019 Jun 22. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 31199118
-
DNA tape measurements of AraC.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Feb;36(2):404-10. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm1030. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18039712 Free PMC article.
-
AraC protein, regulation of the l-arabinose operon in Escherichia coli, and the light switch mechanism of AraC action.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2010 Sep;34(5):779-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00226.x. Epub 2010 Apr 8. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20491933 Review.
Cited by
-
Arabinose Alters Both Local and Distal H-D Exchange Rates in the Escherichia coli AraC Transcriptional Regulator.Biochemistry. 2019 Jul 2;58(26):2875-2882. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00389. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 31199144 Free PMC article.
-
Arginine 37 of Glycine Linker Dictates Regulatory Function of HapR.Front Microbiol. 2020 Aug 21;11:1949. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01949. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32973706 Free PMC article.
-
DOMMINO 2.0: integrating structurally resolved protein-, RNA-, and DNA-mediated macromolecular interactions.Database (Oxford). 2016 Jan 30;2016:bav114. doi: 10.1093/database/bav114. Print 2016. Database (Oxford). 2016. PMID: 26827237 Free PMC article.
-
The LacI-Type transcriptional regulator AraR acts as an L-arabinose-responsive repressor of L-arabinose utilization genes in Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 31831.J Bacteriol. 2014 Jun;196(12):2242-54. doi: 10.1128/JB.01655-14. Epub 2014 Apr 4. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 24706742 Free PMC article.
-
The length of glycine-rich linker in DNA-binding domain is critical for optimal functioning of quorum-sensing master regulatory protein HapR.Mol Genet Genomics. 2014 Dec;289(6):1171-82. doi: 10.1007/s00438-014-0878-5. Epub 2014 Jul 5. Mol Genet Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24997084
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

