Gulosibacter molinativorax ON4T molinate hydrolase, a novel cobalt-dependent amidohydrolase
- PMID: 21840982
- PMCID: PMC3187197
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.05054-11
Gulosibacter molinativorax ON4T molinate hydrolase, a novel cobalt-dependent amidohydrolase
Abstract
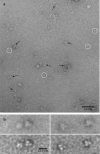
A new pathway of molinate mineralization has recently been described. Among the five members of the mixed culture able to promote such a process, Gulosibacter molinativorax ON4(T) has been observed to promote the initial breakdown of the herbicide into ethanethiol and azepane-1-carboxylate. In the current study, the gene encoding the enzyme responsible for molinate hydrolysis was identified and heterologously expressed, and the resultant active protein was purified and characterized. Nucleotide sequence analysis revealed that the gene encodes a 465-amino-acid protein of the metal-dependent hydrolase A subfamily of the amidohydrolase superfamily with a predicted molecular mass of 50.9 kDa. Molinate hydrolase shares the highest amino acid sequence identity (48 to 50%) with phenylurea hydrolases of Arthrobacter globiformis and Mycobacterium brisbanense. However, in contrast to previously described members of the metal-dependent hydrolase A subfamily, molinate hydrolase contains cobalt as the only active-site metal.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In silico prediction of the enzymes involved in the degradation of the herbicide molinate by Gulosibacter molinativorax ON4T.Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 15;12(1):15502. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-18732-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36109598 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into a bacterial metabolic and detoxifying association responsible for the mineralization of the thiocarbamate herbicide molinate.Microbiology (Reading). 2008 Apr;154(Pt 4):1038-1046. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/015297-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2008. PMID: 18375797
-
Microencapsulation of Gulosibacter molinativorax ON4T cells by a spray-drying process using different biopolymers.J Hazard Mater. 2017 Sep 15;338:85-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.05.018. Epub 2017 May 11. J Hazard Mater. 2017. PMID: 28531662
-
Microbial degradation of the herbicide molinate by defined cultures and in the environment.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013 Dec;97(24):10275-91. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-5316-9. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 24193246 Review.
-
Molinate: rodent reproductive toxicity and its relevance to humans--a review.Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 1998 Apr;27(2):112-8. doi: 10.1006/rtph.1998.1200. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9671566 Review.
Cited by
-
QM Cluster or QM/MM in Computational Enzymology: The Test Case of LigW-Decarboxylase.Front Chem. 2018 Jun 28;6:249. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2018.00249. eCollection 2018. Front Chem. 2018. PMID: 30003076 Free PMC article.
-
In silico prediction of the enzymes involved in the degradation of the herbicide molinate by Gulosibacter molinativorax ON4T.Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 15;12(1):15502. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-18732-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36109598 Free PMC article.
-
HylA, an alternative hydrolase for initiation of catabolism of the phenylurea herbicide linuron in Variovorax sp. strains.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 Sep;79(17):5258-63. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01478-13. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23811502 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary expansion of the amidohydrolase superfamily in bacteria in response to the synthetic compounds molinate and diuron.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 Apr;81(7):2612-24. doi: 10.1128/AEM.04016-14. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25636851 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-guided engineering of molinate hydrolase for the degradation of thiocarbamate pesticides.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 23;10(4):e0123430. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123430. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25905461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barreiros L., et al. 2008. New insights into a bacterial metabolic and detoxifying association responsible for the mineralization of the thiocarbamate herbicide molinate. Microbiology 154:1038–1046 - PubMed
-
- Barreiros L., et al. 2003. A novel pathway for mineralization of the thiocarbamate herbicide molinate by a defined bacterial mixed culture. Environ. Microbiol. 5:944–953 - PubMed
-
- Bradford M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248–254 - PubMed
-
- Caetano-Anollés G. 1993. Amplifying DNA with arbitrary oligonucleotide primers. PCR Methods Appl. 3:85–94 - PubMed
-
- Cochran R. C., Formoli T. A., Pfeifer K. F., Aldous C. N. 1997. Characterization of risks associated with the use of molinate. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 25:146–157 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

