Anacetrapib promotes reverse cholesterol transport and bulk cholesterol excretion in Syrian golden hamsters
- PMID: 21841206
- PMCID: PMC3196228
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M016410
Anacetrapib promotes reverse cholesterol transport and bulk cholesterol excretion in Syrian golden hamsters
Abstract
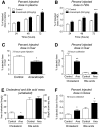
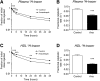
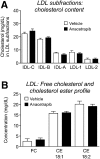
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) transfers cholesteryl ester (CE) and triglyceride between HDL and apoB-containing lipoproteins. Anacetrapib (ANA), a reversible inhibitor of CETP, raises HDL cholesterol (HDL-C) and lowers LDL cholesterol in dyslipidemic patients; however, the effects of ANA on cholesterol/lipoprotein metabolism in a dyslipidemic hamster model have not been demonstrated. To test whether ANA (60 mg/kg/day, 2 weeks) promoted reverse cholesterol transport (RCT), ³H-cholesterol-loaded macrophages were injected and (3)H-tracer levels were measured in HDL, liver, and feces. Compared to controls, ANA inhibited CETP (94%) and increased HDL-C (47%). ³H-tracer in HDL increased by 69% in hamsters treated with ANA, suggesting increased cholesterol efflux from macrophages to HDL. ³H-tracer in fecal cholesterol and bile acids increased by 90% and 57%, respectively, indicating increased macrophage-to-feces RCT. Mass spectrometry analysis of HDL from ANA-treated hamsters revealed an increase in free unlabeled cholesterol and CE. Furthermore, bulk cholesterol and cholic acid were increased in feces from ANA-treated hamsters. Using two independent approaches to assess cholesterol metabolism, the current study demonstrates that CETP inhibition with ANA promotes macrophage-to-feces RCT and results in increased fecal cholesterol/bile acid excretion, further supporting its development as a novel lipid therapy for the treatment of dyslipidemia and atherosclerotic vascular disease.
Figures





References
-
- Gordon T., Castelli W. P., Hjortland M. C., Kannel W. B., Dawber T. R. 1977. High-density lipoprotein as a protective factor against coronary heart-disease - Framingham Study. Am. J. Med. 62: 707–714 - PubMed
-
- Miller N. E., Thelle D. S., Forde O. H., Mjos O. D. 1977. Tromso Heart-Study - high-density lipoprotein and coronary heart-disease - prospective case-control study. Lancet. 1: 965–968 - PubMed
-
- Keys A. 1980. Alpha-lipoprotein (Hdl) cholesterol in the serum and the risk of coronary heart-disease and death. Lancet. 2: 603–606 - PubMed
-
- Jacobs D. R., Mebane I. L., Bangdiwala S. I., Criqui M. H., Tyroler H. A. 1990. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol as a predictor of cardiovascular-disease mortality in men and women - the follow-up-study of the Lipid Research Clinics Prevalence Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 131: 32–47 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

