OSCAR is a collagen receptor that costimulates osteoclastogenesis in DAP12-deficient humans and mice
- PMID: 21841309
- PMCID: PMC3163954
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI45913
OSCAR is a collagen receptor that costimulates osteoclastogenesis in DAP12-deficient humans and mice
Abstract
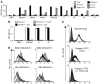
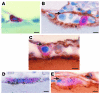
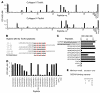
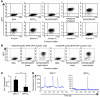
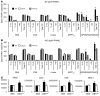
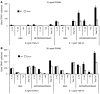
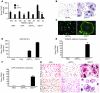
Osteoclasts are terminally differentiated leukocytes that erode the mineralized bone matrix. Osteoclastogenesis requires costimulatory receptor signaling through adaptors containing immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs), such as Fc receptor common γ (FcRγ) and DNAX-activating protein of 12 kDa. Identification of these ITAM-containing receptors and their ligands remains a high research priority, since the stimuli for osteoclastogenesis are only partly defined. Osteoclast-associated receptor (OSCAR) was proposed to be a potent FcRγ-associated costimulatory receptor expressed by preosteoclasts in vitro, but OSCAR lacks a cognate ligand and its role in vivo has been unclear. Using samples from mice and patients deficient in various ITAM signaling pathways, we show here that OSCAR costimulates one of the major FcRγ-associated pathways required for osteoclastogenesis in vivo. Furthermore, we found that OSCAR binds to specific motifs within fibrillar collagens in the ECM that become revealed on nonquiescent bone surfaces in which osteoclasts undergo maturation and terminal differentiation in vivo. OSCAR promoted osteoclastogenesis in vivo, and OSCAR binding to its collagen motif led to signaling that increased numbers of osteoclasts in culture. Thus, our results suggest that ITAM-containing receptors can respond to exposed ligands in collagen, leading to the functional differentiation of leukocytes, which provides what we believe to be a new concept for ITAM regulation of cytokine receptors in different tissue microenvironments.
Figures
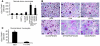
References
-
- Martin TJ. Paracrine regulation of osteoclast formation and activity: milestones in discovery. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2004;4(3):243–253. - PubMed
-
- Kong YY, et al. Activated T cells regulate bone loss and joint destruction in adjuvant arthritis through osteoprotegerin ligand. Nature. 1999;402(6759):304–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

