Human Merkel cell polyomavirus small T antigen is an oncoprotein targeting the 4E-BP1 translation regulator
- PMID: 21841310
- PMCID: PMC3163959
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI46323
Human Merkel cell polyomavirus small T antigen is an oncoprotein targeting the 4E-BP1 translation regulator
Abstract
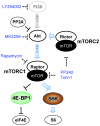
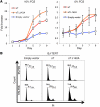
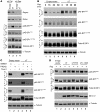
Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCV) is the recently discovered cause of most Merkel cell carcinomas (MCCs), an aggressive form of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Although MCV is known to integrate into the tumor cell genome and to undergo mutation, the molecular mechanisms used by this virus to cause cancer are unknown. Here, we show that MCV small T (sT) antigen is expressed in most MCC tumors, where it is required for tumor cell growth. Unlike the closely related SV40 sT, MCV sT transformed rodent fibroblasts to anchorage- and contact-independent growth and promoted serum-free proliferation of human cells. These effects did not involve protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) inhibition. MCV sT was found to act downstream in the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway to preserve eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1) hyperphosphorylation, resulting in dysregulated cap-dependent translation. MCV sT-associated 4E-BP1 serine 65 hyperphosphorylation was resistant to mTOR complex (mTORC1) and mTORC2 inhibitors. Steady-state phosphorylation of other downstream Akt-mTOR targets, including S6K and 4E-BP2, was also increased by MCV sT. Expression of a constitutively active 4E-BP1 that could not be phosphorylated antagonized the cell transformation activity of MCV sT. Taken together, these experiments showed that 4E-BP1 inhibition is required for MCV transformation. Thus, MCV sT is an oncoprotein, and its effects on dysregulated cap-dependent translation have clinical implications for the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of MCV-related cancers.
Figures
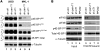
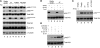

Similar articles
-
Comparison of Akt/mTOR/4E-BP1 pathway signal activation and mutations of PIK3CA in Merkel cell polyomavirus-positive and Merkel cell polyomavirus-negative carcinomas.Hum Pathol. 2015 Feb;46(2):210-6. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2014.07.025. Epub 2014 Oct 23. Hum Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25466966
-
CDK1 substitutes for mTOR kinase to activate mitotic cap-dependent protein translation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 May 12;112(19):5875-82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1505787112. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25883264 Free PMC article.
-
Restricted protein phosphatase 2A targeting by Merkel cell polyomavirus small T antigen.J Virol. 2015 Apr;89(8):4191-200. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00157-15. Epub 2015 Jan 28. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25631078 Free PMC article.
-
4E-BP1, a multifactor regulated multifunctional protein.Cell Cycle. 2016;15(6):781-6. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1151581. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 26901143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reappraisal to the study of 4E-BP1 as an mTOR substrate - A normative critique.Eur J Cell Biol. 2017 Jun;96(4):325-336. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2017.03.013. Epub 2017 Apr 8. Eur J Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28427795 Review.
Cited by
-
Oncogenes and RNA splicing of human tumor viruses.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2014 Sep;3(9):e63. doi: 10.1038/emi.2014.62. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2014. PMID: 26038756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design of potential siRNA molecules for T antigen gene silencing of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus.Bioinformation. 2012;8(19):924-30. doi: 10.6026/97320630008924. Epub 2012 Oct 1. Bioinformation. 2012. PMID: 23144552 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Proteomics Analysis of the JC Virus (JCV) Large and Small Tumor Antigen Interacting Proteins: Large T Primarily Targets the Host Protein Complexes with V-ATPase and Ubiquitin Ligase Activities While Small t Mostly Associates with Those Having Phosphatase and Chromatin-Remodeling Functions.Viruses. 2020 Oct 20;12(10):1192. doi: 10.3390/v12101192. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33092197 Free PMC article.
-
Organotypic Epithelial Raft Cultures as a Three-Dimensional In Vitro Model of Merkel Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Feb 21;14(4):1091. doi: 10.3390/cancers14041091. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205840 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic mTOR activation promotes cell survival in Merkel cell carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2014 Mar 28;344(2):272-281. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.11.005. Epub 2013 Nov 19. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 24262658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gross L. A filterable agent, recovered from Ak leukemic extracts, causing salivary gland carcinomas in C3H mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953;83(2):414–421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

