A universal pathway for kinesin stepping
- PMID: 21841789
- PMCID: PMC3167932
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2104
A universal pathway for kinesin stepping
Abstract
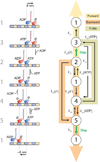
Kinesin-1 is an ATP-driven, processive motor that transports cargo along microtubules in a tightly regulated stepping cycle. Efficient gating mechanisms ensure that the sequence of kinetic events proceeds in the proper order, generating a large number of successive reaction cycles. To study gating, we created two mutant constructs with extended neck-linkers and measured their properties using single-molecule optical trapping and ensemble fluorescence techniques. Owing to a reduction in the inter-head tension, the constructs access an otherwise rarely populated conformational state in which both motor heads remain bound to the microtubule. ATP-dependent, processive backstepping and futile hydrolysis were observed under moderate hindering loads. On the basis of measurements, we formulated a comprehensive model for kinesin motion that incorporates reaction pathways for both forward and backward stepping. In addition to inter-head tension, we found that neck-linker orientation is also responsible for ensuring gating in kinesin.
Figures




References
MAIN REFERENCES
-
- Svoboda K, Schmidt CF, Schnapp BJ, Block SM. Direct observation of kinesin stepping by optical trapping interferometry. Nature. 1993;365:721–727. - PubMed
-
- Kaseda K, Higuchi H, Hirose K. Alternate fast and slow stepping of a heterodimeric kinesin molecule. Nat Cell Biol. 2003;5:1079–1082. - PubMed
-
- Yildiz A, Tomishige M, Vale RD, Selvin PR. Kinesin walks hand-over-hand. Science. 2004;303:676–678. - PubMed
-
- Block SM, Goldstein LS, Schnapp BJ. Bead movement by single kinesin molecules studied with optical tweezers. Nature. 1990;348:348–352. - PubMed
Additional References for Methods
-
- Rosenfeld SS, Xing J, Jefferson GM, Cheung HC, King PH. Measuring kinesin's first step. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:36731–36739. - PubMed
-
- Hiratsuka T. New ribose-modified fluorescent analogs of adenine and guanine nucleotides available as substrates for various enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983;742:496–508. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

