Agonists for the Chemokine Receptor CXCR4
- PMID: 21841963
- PMCID: PMC3155278
- DOI: 10.1021/ml200084n
Agonists for the Chemokine Receptor CXCR4
Abstract
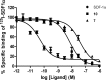
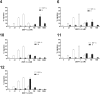
The development of agonists for the chemokine receptor CXCR4 could provide promising therapeutic candidates. On the basis of previously forwarded two site model of chemokine-receptor interactions, we hypothesized that linking the agonistic N-terminus of SDF-1 to the T140 backbone would yield new high-affinity agonists of CXCR4. We developed chimeras with the agonistic SDF-1 N-terminus grafted to a T140 side chain and tested their binding affinity and chemotactic agonist activity. While chimeras with the peptide grafted onto position 12 of T140 remained high-affinity antagonists, those bearing the peptide on position 14 were in part agonists. One chimera was a full CXCR4 agonist with 25 nM affinity, and several chimeras showed low nanomolar affinities with partial agonist activity. Our results confirmed that we have developed high-affinity agonists of CXCR4.
Figures
References
-
- Wu B.; Chien E. Y.; Mol C. D.; Fenalti G.; Liu W.; Katritch V.; Abagyan R.; Brooun A.; Wells P.; Bi F. C.; Hamel D. J.; Kuhn P.; Handel T. M.; Cherezov V.; Stevens R. C. Structures of the CXCR4 chemokine GPCR with small-molecule and cyclic peptide antagonists. Science 2010, 33060071066–1071. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Donzella G. A.; Schols D.; Lin S. W.; Este J. A.; Nagashima K. A.; Maddon P. J.; Allaway G. P.; Sakmar T. P.; Henson G.; De Clercq E.; Moore J. P. AMD3100, a small molecule inhibitor of HIV-1 entry via the CXCR4 co-receptor. Nat. Med. 1998, 4172–77. - PubMed
-
- Schols D.; Este J. A.; Henson G.; De Clercq E. Bicyclams, a class of potent anti-HIV agents, are targeted at the HIV coreceptor fusin/CXCR-4. Antiviral Res. 1997, 353147–156. - PubMed
-
- Zhou N.; Fang J.; Acheampong E.; Mukhtar M.; Pomerantz R. J. Binding of ALX40-4C to APJ, a CNS-based receptor, inhibits its utilization as a co-receptor by HIV-1. Virology 2003, 3121196–203. - PubMed
-
- DeMarco S. J.; Henze H.; Lederer A.; Moehle K.; Mukherjee R.; Romagnoli B.; Robinson J. A.; Brianza F.; Gombert F. O.; Lociuro S.; Ludin C.; Vrijbloed J. W.; Zumbrunn J.; Obrecht J. P.; Obrecht D.; Brondani V.; Hamy F.; Klimkait T. Discovery of novel, highly potent and selective beta-hairpin mimetic CXCR4 inhibitors with excellent anti-HIV activity and pharmacokinetic profiles. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14248396–8404. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information

