Pragmatic vs explanatory trials: the pragmascope tool to help measure differences in protocols of mental health randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 21842618
- PMCID: PMC3182001
- DOI: 10.31887/DCNS.2011.13.2/gtosh
Pragmatic vs explanatory trials: the pragmascope tool to help measure differences in protocols of mental health randomized controlled trials
Abstract
In the pragmatic-explanatory continuum, a randomized controlled trial (RCT) can at one extreme investigate whether a treatment could work in ideal circumstances (explanatory), or at the other extreme, whether it would work in everyday practice (pragmatic). How explanatory or pragmatic a study is can have implications for clinicians, policy makers, patients, researchers, funding bodies, and the public. There is an increasing need for studies to be open and pragmatic; however, explanatory trials are also needed. The previously developed Pragmatic-explanatory continuum indicator summary (PRECIS) was adapted into the Pragmascope tool to assist mental health researchers in designing RCTs, taking the pragmatic-explanatory continuum into account. Ten mental health trial protocols were randomly chosen and scored using the tool by three independent raters. Their results were compared for consistency and the tool was found to be reliable and practical. This preliminary work suggests that evaluating different domains of an RCT at the protocol level is useful, and suggests that using the Pragmascope tool presented here might be a practical way of doing this.
En el continuo pragmático-explicativo, un ensayo controlado randomizado (ECR) puede investigar por una parte si un tratamiento podría funcionar en circunstancias ideales (explicativas) y por otra si podria funcionar en la práctica diaria (pragmático). Cuan explicativo o pragmático sea un estudio, puede tener repercusiones para los clinicos, los políticos, los pacientes, los investigadores, los organismos de financiamiento y el público. Hay una necesidad creciente de que los estudios sean abiertos y pragmáticos; sin embargo, también son necesarios los ensayos explicativos. PRECIS, el resumen del indicador del continuo pragmático-explicativo que se había desarrollado con anterioridad, se adaptó al instrumento Pragmascope para ayudar a los investigadores de salud mental en los diseños de ECR, tomando en consideración el continuo pragmático-explicativo. Se eligieron randomizadamente diez protocolos de ensayos de salud mental y se les asignó puntaje mediante el instrumento por tres evaluadores independientes. Sus resultados se compararon en cuanto a consistencia y se encontró que el instrumento fue confiable y práctico. Este trabajo preliminar sugiere que es útil la evaluación de diferentes aspectos de un ECR a nivel del protocolo y propone que el empleo del instrumento Pragmascope presentado aquí sería una forma práctica de hacerlo.
Dans le continuum pragmatique-explicatif, une étude contrôlée randomisée (ECR) peut d'un côté analyser l'efficacité d'un traitement en circonstances idéales (explicatives) ou d'un autre côté son efficacité dans la pratique quotidienne (pragmatique). Qu'une étude soit explicative ou pragmatique, elle peut avoir des implications pour les médecins, les responsables politiques, les patients, les chercheurs, les organismes de financement et le public. Les études doivent de plus en plus être ouvertes et pragmatiques, mais les études explicatives sont aussi nécessaires. L'indicateur de continuum pragmatique - explicatif PRECIS (Pragmatic-explanatory conti nuum indicator summary) développé antérieurement a été adapté sous forme de l'outil PRAGMASCOPE pour aider les chercheurs en santé mentale à concevoir des ECR, en prenant en compte ledit continuum. Dix protocoles d'études en santé mentale ont été choisis et cotés au hasard grâce à l'outil, par trois évaluateurs indépendants. Leurs résultats ont été comparés pour évaluer leur cohérence et l'outil s'est avéré fiable et pratique. Ce travail préliminaire suggère que l'évaluation des différents domaines des ECR au niveau du protocole est utile et que l'utilisation du PRAGMASCOPE présenté ici pourrait être un moyen pratique de le faire.
Figures
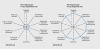


References
-
- WHO. Evaluation of methods for the treatment of mental disorders. Report of a WHO Scientific Group on the Treatment of Psychiatric Disorders. World Health Organization Technical Report Series. 1991;812:1–75. - PubMed
-
- Medical Research C. Streptomycin treatment of tuberculous meningitis. Lancet. 1948;1:582–596. - PubMed
-
- Documenting the evolution of fair tests. Available at: http://www.jameslindlibrary.org/. - PubMed
-
- Turner T. Chlorpromazine: unlocking psychosis. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed). 2007;334(suppl 1):s7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
