Communication: Iteration-free, weighted histogram analysis method in terms of intensive variables
- PMID: 21842919
- PMCID: PMC3166335
- DOI: 10.1063/1.3626150
Communication: Iteration-free, weighted histogram analysis method in terms of intensive variables
Abstract
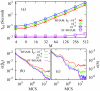
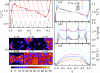
We present an iteration-free weighted histogram method in terms of intensive variables that directly determines the inverse statistical temperature, β(S) = ∂S/∂E, with S the microcanonical entropy. The method eliminates iterative evaluations of the partition functions intrinsic to the conventional approach and leads to a dramatic acceleration of the posterior analysis of combining statistically independent simulations with no loss in accuracy. The synergistic combination of the method with generalized ensemble weights provides insights into the nature of the underlying phase transitions via signatures in β(S) characteristic of finite size systems. The versatility and accuracy of the method is illustrated for the Ising and Potts models.
Figures

References
-
- Newman M. E. J. and Barkema G. T., Monte Carlo Methods in Statistical Physics (Clarendon, Oxford, 1999).
-
- Frenkel D. and Smit B., Understanding Molecular Simulation: From Algorithms to Applications (Academic, San Diego, 1996).
-
- Kumar S., Bouzuda D., Swendsen R. H., Kollman P. A., and Rosenberg J. M., J. Comput. Chem. 13, 1011 (1992).10.1002/jcc.540130812 - DOI
-
- Souaille M. and Roux B., Comput. Phys. Commun. 135, 40 (2001).10.1016/S0010-4655(00)00215-0 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

