Vascular cell-adhesion molecule-1 plays a central role in the proangiogenic effects of oxidative stress
- PMID: 21844360
- PMCID: PMC3167513
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1012859108
Vascular cell-adhesion molecule-1 plays a central role in the proangiogenic effects of oxidative stress
Abstract
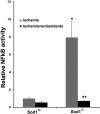
Oxidative stress exacerbates neovascularization (NV) in many disease processes. In this study we investigated the mechanism of that effect. Mice deficient in superoxide dismutase 1 (Sod1(-/-) mice) have increased oxidative stress and show severe ocular NV that is reduced to baseline by antioxidants. Compared with wild-type mice with ischemic retinopathy, Sod1(-/-) mice with ischemic retinopathy had increased expression of several NF-κB-responsive genes, but expression of vascular cell-adhesion molecule-1 (Vcam1) was particularly high. Intraocular injection of anti-VCAM-1 antibody eliminated the excessive ischemia-induced retinal NV. Elements that contributed to oxidative stress-induced worsening of retinal NV that were abrogated by blockade of VCAM-1 included increases in leukostasis, influx of bone marrow-derived cells, and capillary closure. Compared with ischemia alone, ischemia plus oxidative stress resulted in increased expression of several HIF-1-responsive genes caused in part by VCAM-1-induced worsening of nonperfusion and, hence, ischemia, because anti-VCAM-1 significantly reduced the increased expression of all but one of the genes. These data explain why oxidative stress worsens ischemia-induced retinal NV and may be relevant to other neovascular diseases in which oxidative stress has been implicated. The data also suggest that antagonism of VCAM-1 provides a potential therapy to combat worsening of neovascular diseases by oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Semenza GL. HIF-1: Mediator of physiological and pathophysiological responses to hypoxia. J Appl Physiol. 2000;88:1474–1480. - PubMed
-
- Ozaki H, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor-1α is increased in ischemic retina: Temporal and spatial correlation with VEGF expression. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999;40:182–189. - PubMed
-
- Kelly BD, et al. Cell type-specific regulation of angiogenic growth factor gene expression and induction of angiogenesis in nonischemic tissue by a constitutively active form of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Circ Res. 2003;93:1074–1081. - PubMed
-
- Vinores SA, et al. Implication of the hypoxia response element of the Vegf promoter in mouse models of retinal and choroidal neovascularization, but not retinal vascular development. J Cell Physiol. 2006;206:749–758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

