Seasonal variation of water quality and phytoplankton response patterns in Daya Bay, China
- PMID: 21845168
- PMCID: PMC3155339
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph8072951
Seasonal variation of water quality and phytoplankton response patterns in Daya Bay, China
Abstract
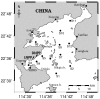
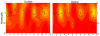
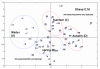
Data collected from 12 stations in Daya Bay in different seasons in 2002 revealed the relation between water quality and phytoplankton response patterns. The results showed that Daya Bay could be divided into wet and dry seasons by multivariate statistical analysis. Principal component analysis indicated that temperature, chlorophyll a and nutrients were important components during the wet season (summer and autumn). The salinity and dissolved oxygen were the main environmental factors in the dry season (winter and spring). According to non-metric multidimensional scaling, there was a shift from the large diatoms in the dry season to the smaller line-chain taxa in the wet season with the condition of a high dissolved inorganic nitrogen and nitrogen to phosphorous concentration ratio. Nutrient changes can thus alter the phytoplankton community composition and biomass, especially near the aquaculture farm areas. There was no evidence of an effect of thermal water from the nearby nuclear power plants on the observed changes in phytoplankton community and biomass in 2002.
Keywords: Daya Bay (DYB); South China Sea; human activities; multivariate analysis; phytoplankton; water quality.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Modeling the ecosystem response of the semi-closed Daya Bay to the thermal discharge from two nearby nuclear power plants.Ecotoxicology. 2020 Aug;29(6):736-750. doi: 10.1007/s10646-020-02229-w. Epub 2020 May 21. Ecotoxicology. 2020. PMID: 32440859
-
Variation of phytoplankton biomass and primary production in Daya Bay during spring and summer.Mar Pollut Bull. 2004 Dec;49(11-12):1036-44. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.07.008. Mar Pollut Bull. 2004. PMID: 15556190
-
Phytoplankton community, structure and succession delineated by partial least square regression in Daya Bay, South China Sea.Ecotoxicology. 2020 Aug;29(6):751-761. doi: 10.1007/s10646-020-02188-2. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Ecotoxicology. 2020. PMID: 32189146
-
Dynamics of alkaline phosphatase activity in relation to phytoplankton and bacteria in a coastal embayment Daya Bay, South China.Mar Pollut Bull. 2018 Jun;131(Pt A):736-744. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.05.008. Mar Pollut Bull. 2018. PMID: 29887001
-
Long-term changes of nutrients and biocenoses indicating the anthropogenic influences on ecosystem in Jiaozhou Bay and Daya Bay, China.Mar Pollut Bull. 2021 Jul;168:112406. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112406. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Mar Pollut Bull. 2021. PMID: 33932842 Review.
Cited by
-
Variation of phytoplankton community structure from the Pearl River estuary to South China Sea.Ecotoxicology. 2015 Oct;24(7-8):1442-9. doi: 10.1007/s10646-015-1494-9. Epub 2015 May 23. Ecotoxicology. 2015. PMID: 26002220
-
Eutrophication assessment and management methodology of multiple pollution sources of a landscape lake in North China.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2013 Jun;20(6):3877-89. doi: 10.1007/s11356-012-1331-0. Epub 2012 Nov 27. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23184129
-
Spatial variation of phytoplankton community structure in Daya Bay, China.Ecotoxicology. 2015 Oct;24(7-8):1450-8. doi: 10.1007/s10646-015-1471-3. Epub 2015 May 9. Ecotoxicology. 2015. PMID: 25956980
-
Carbon and Nitrogen Burial and Response to Climate Change and Anthropogenic Disturbance in Chaohu Lake, China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 Dec 4;15(12):2734. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15122734. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30518045 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship between Phytoplankton Evenness and Copepod Abundance in Lake Nansihu, China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016 Aug 31;13(9):855. doi: 10.3390/ijerph13090855. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016. PMID: 27589782 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu ML, Wang YS. Using chemometrics to evaluate anthropogenic effects in Daya Bay, China. Estuarine Coastal Shelf Sci. 2007;72:732–742.
-
- Jordan TE, Correll DL, Weller DE. Effects of agriculture on discharges of nutrients from Coastal Plain watersheds of Chesapeake Bay. J Environ Q. 1997;26:836–848.
-
- Tsujimoto A, Nomura R, Yasuhara M, Yamazaki H, Yoshikawa S. Impact of eutrophication on shallow marine benthic foraminifers over the last 150 years in Osaka Bay, Japan. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2006;60:258–268.
-
- MÖLlmann C, Diekmann R, MÜLler-Karulis B, Kornilovs G, Plikshs M, Axe P. Reorganization of a large marine ecosystem due to atmospheric and anthropogenic pressure: A discontinuous regime shift in the Central Baltic Sea. Glob. Change Biol. 2009;15:1377–1393.
-
- Lapointe BE, Clark MW. Nutrient inputs from the watershed and coastal eutrophication in the Florida Keys. Estuaries. 1992;15:465–476.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

