Integrated miRNA and mRNA expression profiling of mouse mammary tumor models identifies miRNA signatures associated with mammary tumor lineage
- PMID: 21846369
- PMCID: PMC3245617
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2011-12-8-r77
Integrated miRNA and mRNA expression profiling of mouse mammary tumor models identifies miRNA signatures associated with mammary tumor lineage
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, non-coding, endogenous RNAs involved in regulating gene expression and protein translation. miRNA expression profiling of human breast cancers has identified miRNAs related to the clinical diversity of the disease and potentially provides novel diagnostic and prognostic tools for breast cancer therapy. In order to further understand the associations between oncogenic drivers and miRNA expression in sub-types of breast cancer, we performed miRNA expression profiling on mammary tumors from eight well-characterized genetically engineered mouse (GEM) models of human breast cancer, including MMTV-H-Ras, -Her2/neu, -c-Myc, -PymT, -Wnt1 and C3(1)/SV40 T/t-antigen transgenic mice, BRCA1(fl/fl);p53(+/-);MMTV-cre knock-out mice and the p53(fl/fl);MMTV-cre transplant model.
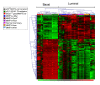
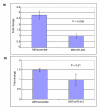
Results: miRNA expression patterns classified mouse mammary tumors according to luminal or basal tumor subtypes. Many miRNAs found in luminal tumors are expressed during normal mammary development. miR-135b, miR-505 and miR-155 are expressed in both basal human and mouse mammary tumors and many basal-associated miRNAs have not been previously characterized. miRNAs associated with the initiating oncogenic event driving tumorigenesis were also identified. miR-10b, -148a, -150, -199a and -486 were only expressed in normal mammary epithelium and not tumors, suggesting that they may have tumor suppressor activities. Integrated miRNA and mRNA gene expression analyses greatly improved the identification of miRNA targets from potential targets identified in silico.
Conclusions: This is the first large-scale miRNA gene expression study across a variety of relevant GEM models of human breast cancer demonstrating that miRNA expression is highly associated with mammary tumor lineage, differentiation and oncogenic pathways.
Figures


Similar articles
-
FAK activates AKT-mTOR signaling to promote the growth and progression of MMTV-Wnt1-driven basal-like mammary tumors.Breast Cancer Res. 2020 Jun 3;22(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s13058-020-01298-3. Breast Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32493400 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of miR-489 derails mammary hierarchy structure and inhibits HER2/neu-induced tumorigenesis.Oncogene. 2019 Jan;38(3):445-453. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0439-1. Epub 2018 Aug 13. Oncogene. 2019. PMID: 30104710 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA expression and gene regulation drive breast cancer progression and metastasis in PyMT mice.Breast Cancer Res. 2016 Jul 22;18(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0735-z. Breast Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27449149 Free PMC article.
-
[microRNA expression in breast development and breast cancer].Pathologe. 2013 Nov;34 Suppl 2:195-200. doi: 10.1007/s00292-013-1878-7. Pathologe. 2013. PMID: 24196612 Review. German.
-
MMTV mouse models and the diagnostic values of MMTV-like sequences in human breast cancer.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2009 Jul;9(5):423-40. doi: 10.1586/erm.09.31. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2009. PMID: 19580428 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sox11 regulates mammary tumour-initiating and metastatic capacity in Brca1-deficient mouse mammary tumour cells.Dis Model Mech. 2021 May 1;14(5):dmm046037. doi: 10.1242/dmm.046037. Epub 2021 May 10. Dis Model Mech. 2021. PMID: 33969421 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated microRNA and mRNA responses to acute human left ventricular ischemia.Physiol Genomics. 2015 Oct;47(10):455-62. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00049.2015. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Physiol Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26175501 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Parathyroid hormone 1 receptor signaling mediates breast cancer metastasis to bone in mice.JCI Insight. 2023 Mar 8;8(5):e157390. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.157390. JCI Insight. 2023. PMID: 36692956 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting miRNAs and Other Non-Coding RNAs as a Therapeutic Approach: An Update.Noncoding RNA. 2023 Apr 13;9(2):27. doi: 10.3390/ncrna9020027. Noncoding RNA. 2023. PMID: 37104009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomic dynamics of breast cancer progression in the MMTV-PyMT mouse model.BMC Genomics. 2017 Feb 17;18(1):185. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3563-3. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28212608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M, Menard S, Palazzo JP, Rosenberg A, Musiani P, Volinia S, Nenci I, Calin GA, Querzoli P, Negrini M, Croce CM. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:7065–7070. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1783. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, Prueitt RL, Yanaihara N, Lanza G, Scarpa A, Vecchione A, Negrini M, Harris CC, Croce CM. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:2257–2261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510565103. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

