Calcium microdomains at the immunological synapse: how ORAI channels, mitochondria and calcium pumps generate local calcium signals for efficient T-cell activation
- PMID: 21847095
- PMCID: PMC3209779
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.289
Calcium microdomains at the immunological synapse: how ORAI channels, mitochondria and calcium pumps generate local calcium signals for efficient T-cell activation
Abstract
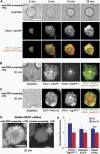
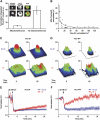
Cell polarization enables restriction of signalling into microdomains. Polarization of lymphocytes following formation of a mature immunological synapse (IS) is essential for calcium-dependent T-cell activation. Here, we analyse calcium microdomains at the IS with total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy. We find that the subplasmalemmal calcium signal following IS formation is sufficiently low to prevent calcium-dependent inactivation of ORAI channels. This is achieved by localizing mitochondria close to ORAI channels. Furthermore, we find that plasma membrane calcium ATPases (PMCAs) are re-distributed into areas beneath mitochondria, which prevented PMCA up-modulation and decreased calcium export locally. This nano-scale distribution-only induced following IS formation-maximizes the efficiency of calcium influx through ORAI channels while it decreases calcium clearance by PMCA, resulting in a more sustained NFAT activity and subsequent activation of T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Mitochondria positioning controls local calcium influx in T cells.J Immunol. 2010 Jan 1;184(1):184-90. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902872. Epub 2009 Nov 30. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 19949095
-
Morphological changes of T cells following formation of the immunological synapse modulate intracellular calcium signals.Cell Calcium. 2009 Feb;45(2):109-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2008.07.003. Epub 2008 Sep 13. Cell Calcium. 2009. PMID: 18789821
-
Cytoskeleton rotation relocates mitochondria to the immunological synapse and increases calcium signals.Cell Calcium. 2016 Nov;60(5):309-321. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2016.06.007. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Cell Calcium. 2016. PMID: 27451384
-
Mitochondrial dynamics and their impact on T cell function.Cell Calcium. 2012 Jul;52(1):57-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2012.02.005. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Cell Calcium. 2012. PMID: 22425631 Review.
-
The immunological synapse controls local and global calcium signals in T lymphocytes.Immunol Rev. 2009 Sep;231(1):132-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00811.x. Immunol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19754894 Review.
Cited by
-
The functional contribution of calcium ion flux heterogeneity in T cells.Immunol Cell Biol. 2015 Sep;93(8):694-704. doi: 10.1038/icb.2015.34. Epub 2015 Mar 31. Immunol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25823995 Review.
-
Ca2+ signaling in T lymphocytes: the interplay of the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, membrane potential, and CRAC channels on transcription factor activation.Heliyon. 2020 Mar 7;6(3):e03526. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03526. eCollection 2020 Mar. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32181396 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Kv10.1 Channels Sensitizes Mitochondria of Cancer Cells to Antimetabolic Agents.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Apr 9;12(4):920. doi: 10.3390/cancers12040920. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32283712 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial junctions with cellular organelles: Ca2+ signalling perspective.Pflugers Arch. 2018 Aug;470(8):1181-1192. doi: 10.1007/s00424-018-2179-z. Epub 2018 Jul 7. Pflugers Arch. 2018. PMID: 29982949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium signals regulate the functional differentiation of thymic iNKT cells.EMBO J. 2021 Aug 16;40(16):e107901. doi: 10.15252/embj.2021107901. Epub 2021 Jun 25. EMBO J. 2021. PMID: 34169542 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abarca-Rojano E, Muñiz-Hernández S, Moreno-Altamirano MM, Mondragón-Flores R, Enriquez-Rincón F, Sánchez-García FJ (2009) Re-organization of mitochondria at the NK cell immune synapse. Immunol Lett 122: 18–25 - PubMed
-
- Bauer MC, O’Connell D, Cahill DJ, Linse S (2008) Calmodulin binding to the polybasic C-termini of STIM proteins involved in store-operated calcium entry. Biochemistry 47: 6089–6091 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

