Quality control parameters on a large dataset of regionally dissected human control brains for whole genome expression studies
- PMID: 21848658
- PMCID: PMC3664422
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07432.x
Quality control parameters on a large dataset of regionally dissected human control brains for whole genome expression studies
Abstract
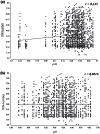
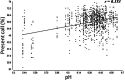
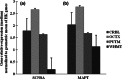
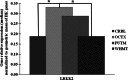
We are building an open-access database of regional human brain expression designed to allow the genome-wide assessment of genetic variability on expression. Array and RNA sequencing technologies make assessment of genome-wide expression possible. Human brain tissue is a challenging source for this work because it can only be obtained several and variable hours post-mortem and after varying agonal states. These variables alter RNA integrity in a complex manner. In this report, we assess the effect of post-mortem delay, agonal state and age on gene expression, and the utility of pH and RNA integrity number as predictors of gene expression as measured on 1266 Affymetrix Exon Arrays. We assessed the accuracy of the array data using QuantiGene, as an independent non-PCR-based method. These quality control parameters will allow database users to assess data accuracy. We report that within the parameters of this study post-mortem delay, agonal state and age have little impact on array quality, array data are robust to variable RNA integrity, and brain pH has only a small effect on array performance. QuantiGene gave very similar expression profiles as array data. This study is the first step in our initiative to make human, regional brain expression freely available.
© 2011 The Authors. Journal of Neurochemistry © 2011 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Figures


References
-
- Barrachina M, Castano E, Ferrer I. TaqMan PCR assay in the control of RNA normalization in human post-mortem brain tissue. Neurochem. Int. 2006;49:276–284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

