Comparative analysis of USA300 virulence determinants in a rabbit model of skin and soft tissue infection
- PMID: 21849291
- PMCID: PMC3156927
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jir441
Comparative analysis of USA300 virulence determinants in a rabbit model of skin and soft tissue infection
Abstract
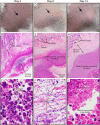
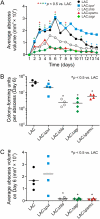
Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) infections are frequently associated with strains harboring genes encoding Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL). The role of PVL in the success of the epidemic CA-MRSA strain USA300 remains unknown. Here we developed a skin and soft tissue infection model in rabbits to test the hypothesis that PVL contributes to USA300 pathogenesis and compare it with well-established virulence determinants: alpha-hemolysin (Hla), phenol-soluble modulin-alpha peptides (PSMα), and accessory gene regulator (Agr). The data indicate that Hla, PSMα, and Agr contribute to the pathogenesis of USA300 skin infections in rabbits, whereas a role for PVL could not be detected.
Figures
References
-
- Moran GJ, Krishnadasan A, Gorwitz RJ, et al. Methicillin-resistant S. aureus infections among patients in the emergency department. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:666–74. - PubMed
-
- King MD, Humphrey BJ, Wang YF, Kourbatova EV, Ray SM, Blumberg HM. Emergence of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA300 clone as the predominant cause of skin and soft-tissue infections. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144:309–17. - PubMed
-
- Voyich JM, Braughton KR, Sturdevant DE, et al. Insights into mechanisms used by Staphylococcus aureus to avoid destruction by human neutrophils. J Immunol. 2005;175:3907–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

