Converging PET and fMRI evidence for a common area involved in human focal epilepsies
- PMID: 21849655
- PMCID: PMC3162638
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31822c90f2
Converging PET and fMRI evidence for a common area involved in human focal epilepsies
Abstract
Objectives: Experiments in animal models have identified specific subcortical anatomic circuits, which are critically involved in the pathogenesis and control of seizure activity. However, whether such anatomic substrates also exist in human epilepsy is not known.
Methods: We studied 2 separate groups of patients with focal epilepsies arising from any cortical location using either simultaneous EEG-fMRI (n = 19 patients) or [¹¹C]flumazenil PET (n = 18).
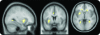
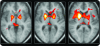
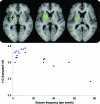
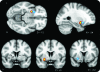
Results: Time-locked with the interictal epileptiform discharges, we found significant hemodynamic increases common to all patients near the frontal piriform cortex ipsilateral to the presumed cortical focus. GABA(A) receptor binding in the same area was reduced in patients with more frequent seizures.
Conclusions: Our findings of cerebral blood flow and GABAergic changes, irrespective of where interictal or ictal activity occurs in the cortex, suggest that this area of the human primary olfactory cortex may be an attractive new target for epilepsy therapy, including neurosurgery, electrical stimulation, and focal drug delivery.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantitative analysis of simultaneous EEG features during PET studies for childhood partial epilepsy.Yonsei Med J. 2013 May 1;54(3):572-7. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.3.572. Yonsei Med J. 2013. PMID: 23549798 Free PMC article.
-
Focal decreases of cortical GABAA receptor binding remote from the primary seizure focus: what do they indicate?Epilepsia. 2009 Feb;50(2):240-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01721.x. Epub 2008 Jul 14. Epilepsia. 2009. PMID: 18637829 Free PMC article.
-
PET/MRI and PET/MRI/SISCOM coregistration in the presurgical evaluation of refractory focal epilepsy.Epilepsy Res. 2015 Mar;111:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2014.12.011. Epub 2015 Jan 3. Epilepsy Res. 2015. PMID: 25769367
-
Functional imaging of the piriform cortex in focal epilepsy.Exp Neurol. 2020 Aug;330:113305. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113305. Epub 2020 Apr 9. Exp Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32278645 Review.
-
[Morphological and functional neuro-imaging of surgical partial epilepsies in adults].Rev Neurol (Paris). 1996 Aug-Sep;152(8-9):501-16. Rev Neurol (Paris). 1996. PMID: 8991172 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Increased segregation of brain networks in focal epilepsy: An fMRI graph theory finding.Neuroimage Clin. 2015 May 22;8:536-42. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.05.009. eCollection 2015. Neuroimage Clin. 2015. PMID: 26110111 Free PMC article.
-
Networks involved in seizure initiation. A reading epilepsy case studied with EEG-fMRI and MEG.Neurology. 2012 Jul 17;79(3):249-53. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31825fdf3a. Epub 2012 Jul 3. Neurology. 2012. PMID: 22764255 Free PMC article.
-
Spectral entropy indicates electrophysiological and hemodynamic changes in drug-resistant epilepsy - A multimodal MREG study.Neuroimage Clin. 2019;22:101763. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2019.101763. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Neuroimage Clin. 2019. PMID: 30927607 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of PET imaging for the localization of epileptogenic zone in patients with epilepsy: a meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2021 Aug;31(8):6353-6366. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07645-4. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33523306 Review.
-
Effects of carbamazepine and lamotrigine on functional magnetic resonance imaging cognitive networks.Epilepsia. 2018 Jul;59(7):1362-1371. doi: 10.1111/epi.14448. Epub 2018 Jun 13. Epilepsia. 2018. PMID: 29897625 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Gale K, Zhong P, Miller LP, Murray TF. Amino acid neurotransmitter interactions in ‘area tempestas': an epileptogenic trigger zone in the deep prepiriform cortex. Epilepsy Res Suppl 1992;8:229–234 - PubMed
-
- Löscher W, Ebert U. The role of the piriform cortex in kindling. Prog Neurobiol 1996;50:427–818 - PubMed
-
- Gale K. Chemoconvulsant seizures: advantages of focally-evoked seizure models. Ital J Neurol Sci 1995;16:17–25 - PubMed
-
- Piredda S, Gale K. A crucial epileptogenic site in the deep prepiriform cortex. Nature 1985;317:623–625 - PubMed
-
- Steriade M. Sleep, epilepsy and thalamic reticular inhibitory neurons. Trends Neurosci 2005;28:317–324 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
