A genomewide linkage scan of cocaine dependence and major depressive episode in two populations
- PMID: 21849985
- PMCID: PMC3194068
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2011.122
A genomewide linkage scan of cocaine dependence and major depressive episode in two populations
Abstract
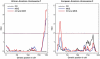
Cocaine dependence (CD) and major depressive episode (MDE) frequently co-occur with poorer treatment outcome and higher relapse risk. Shared genetic risk was affirmed; to date, there have been no reports of genomewide linkage scans (GWLSs) surveying the susceptibility regions for comorbid CD and MDE (CD-MDE). We aimed to identify chromosomal regions and candidate genes susceptible to CD, MDE, and CD-MDE in African Americans (AAs) and European Americans (EAs). A total of 1896 individuals were recruited from 384 AA and 355 EA families, each with at least a sibling-pair with CD and/or opioid dependence. Array-based genotyping of about 6000 single-nucleotide polymorphisms was completed for all individuals. Parametric and non-parametric genomewide linkage analyses were performed. We found a genomewide-significant linkage peak on chromosome 7 at 183.4 cM for non-parametric analysis of CD-MDE in AAs (lod=3.8, genomewide empirical p=0.016; point-wise p=0.00001). A nearly genomewide significant linkage was identified for CD-MDE in EAs on chromosome 5 at 14.3 cM (logarithm of odds (lod)=2.95, genomewide empirical p=0.055; point-wise p=0.00012). Parametric analysis corroborated the findings in these two regions and improved the support for the peak on chromosome 5 so that it reached genomewide significance (heterogeneity lod=3.28, genomewide empirical p=0.046; point-wise p=0.00053). This is the first GWLS for CD-MDE. The genomewide significant linkage regions on chromosomes 5 and 7 harbor four particularly promising candidate genes: SRD5A1, UBE3C, PTPRN2, and VIPR2. Replication of the linkage findings in other populations is warranted, as is a focused analysis of the genes located in the linkage regions implicated here.
Figures


References
-
- Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR. Merlin--rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat Genet. 2002;30:97–101. - PubMed
-
- Andretic R, Chaney S, Hirsh J. Requirement of circadian genes for cocaine sensitization in Drosophila. Science. 1999;285:1066–1068. - PubMed
-
- Camp NJ, Lowry MR, Richards RL, Plenk AM, Carter C, Hensel CH, et al. Genome-wide linkage analyses of extended Utah pedigrees identifies loci that influence recurrent, early-onset major depression and anxiety disorders. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2005;135:85–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 DA18432/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012849/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 NS051869-02S1/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA12849/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA018432/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA011330/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA12690/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DA24758/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012690/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 NS051869/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA11330/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HG065403/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DA024758/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

