Critical role of SDF-1α-induced progenitor cell recruitment and macrophage VEGF production in the experimental corneal neovascularization
- PMID: 21850188
- PMCID: PMC3156784
Critical role of SDF-1α-induced progenitor cell recruitment and macrophage VEGF production in the experimental corneal neovascularization
Abstract
Purpose: To address the roles of the stromal derived factor-1 (SDF-1) α in the course of experimental corneal neovascularization (CNV).
Methods: CNV was induced by alkali injury and compared in SDF-1α- or vehicle-treated mice two weeks after injury. Angiogenic factor expression in the early phase after injury was quantified by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Progenitor cell, macrophage, and monocyte intracorneal accumulation in the early phase after injury was evaluated by flow cytometric analysis.
Results: The mRNA expression of SDF-1α was augmented, together with infiltration of c-kit-positive progenitor cells in the corneas after the alkali injury. Compared with vehicle-treated mice, SDF-1α-treated mice exhibited enhanced CNV two weeks after injury, as evidenced by enlarged cluster of differentiation 31 (CD31)-positive areas. Concomitantly, the intracorneal infiltration of c-kit-positive progenitor cells but not F4/80+ macrophages or Ly-6G+ monocytes was significantly enhanced in SDF-1α-treated mice compared to vehicle-treated mice. SDF-1α enhanced vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression by murine peritoneal macrophages. Enhancement in intraocular VEGF expression was greater in SDF-1α-treated mice than in control mice after injury. Moreover, local administration of C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) antagonist after alkali injury reduced alkali-induced CNV.
Conclusions: SDF-1α-treated mice exhibited enhanced alkali-induced CNV through enhanced intracorneal progenitor cell infiltration and increased VEGF expression by macrophages.
Figures





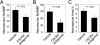
References
-
- Ambati BK, Nozaki M, Singh N, Takeda A, Jani PD, Suthar T, Albuquerque RJC, Richter E, Sakurai E, Newcomb MT, Kleinman ME, Caldwell RB, Lin Q, Ogura Y, Orecchia A, Samuelson DA, Agnew DW, St. Leger J, Green WR, Mahasreshti PJ, Curiel DT, Kwan D, Marsh H, Ikeda S, Leiper LJ, Collinson JM, Bogdanovich S, Khurana TS, Shibuya M, Baldwin ME, Ferrara N, Gerber H-P, DeFalco S, Witta J, Baffi JZ, Raisler BJ, Ambati J. Corneal avascularity is due to soluble VEGF receptor-1. Nature. 2006;443:993–7. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cursiefen C, Masli S, Ng TF, Dana MR, Bornstein P, Lawler J, Streilein JW. Roles of thrombospondin-1 and −2 in regulating corneal and iris angiogenesis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004;45:1117–24. - PubMed
-
- Gao G, Ma J. Tipping the balance for angiogenic disorders. Drug Discov Today. 2002;7:171–2. - PubMed
-
- Zhang SX, Ma JX. Ocular neovascularization: Implication of endogenous angiogenic inhibitors and potential therapy. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2007;26:1–37. - PubMed
-
- Lu P, Li L, Mukaida N, Zhang X. Alkali-induced corneal neovascularization is independent of CXCR2-mediated neutrophil infiltration. Cornea. 2007;26:199–206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
