SLOB, a SLOWPOKE channel binding protein, regulates insulin pathway signaling and metabolism in Drosophila
- PMID: 21850269
- PMCID: PMC3151297
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023343
SLOB, a SLOWPOKE channel binding protein, regulates insulin pathway signaling and metabolism in Drosophila
Abstract
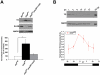
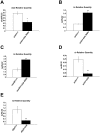
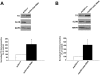
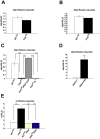
There is ample evidence that ion channel modulation by accessory proteins within a macromolecular complex can regulate channel activity and thereby impact neuronal excitability. However, the downstream consequences of ion channel modulation remain largely undetermined. The Drosophila melanogaster large conductance calcium-activated potassium channel SLOWPOKE (SLO) undergoes modulation via its binding partner SLO-binding protein (SLOB). Regulation of SLO by SLOB influences the voltage dependence of SLO activation and modulates synaptic transmission. SLO and SLOB are expressed especially prominently in median neurosecretory cells (mNSCs) in the pars intercerebralis (PI) region of the brain; these cells also express and secrete Drosophila insulin like peptides (dILPs). Previously, we found that flies lacking SLOB exhibit increased resistance to starvation, and we reasoned that SLOB may regulate aspects of insulin signaling and metabolism. Here we investigate the role of SLOB in metabolism and find that slob null flies exhibit changes in energy storage and insulin pathway signaling. In addition, slob null flies have decreased levels of dilp3 and increased levels of takeout, a gene known to be involved in feeding and metabolism. Targeted expression of SLOB to mNSCs rescues these alterations in gene expression, as well as the metabolic phenotypes. Analysis of fly lines mutant for both slob and slo indicate that the effect of SLOB on metabolism and gene expression is via SLO. We propose that modulation of SLO by SLOB regulates neurotransmission in mNSCs, influencing downstream insulin pathway signaling and metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Slob, a Slowpoke channel-binding protein, modulates synaptic transmission.J Gen Physiol. 2011 Feb;137(2):225-38. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201010439. J Gen Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21282401 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo role of a potassium channel-binding protein in regulating neuronal excitability and behavior.J Neurosci. 2009 Oct 21;29(42):13328-37. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3024-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19846720 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and function of variants of slob, slowpoke channel binding protein, in Drosophila.J Neurophysiol. 2006 Mar;95(3):1957-65. doi: 10.1152/jn.00427.2005. Epub 2005 Dec 7. J Neurophysiol. 2006. PMID: 16339006
-
High-conductance potassium channels of the SLO family.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006 Dec;7(12):921-31. doi: 10.1038/nrn1992. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17115074 Review.
-
Factors that regulate expression patterns of insulin-like peptides and their association with physiological and metabolic traits in Drosophila.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2021 Aug;135:103609. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2021.103609. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34146686 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of insect behavior via the insulin-signaling pathway.Front Physiol. 2013 Dec 3;4:353. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00353. Front Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24348428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary glucose regulates yeast consumption in adult Drosophila males.Front Physiol. 2014 Dec 22;5:504. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00504. eCollection 2014. Front Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25566097 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and Localization of Sol g 2.1 Protein from Solenopsis geminata Fire Ant Venom in the Central Nervous System of Injected Crickets (Acheta domestica).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 1;24(19):14814. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914814. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834262 Free PMC article.
-
Using Drosophila to discover mechanisms underlying type 2 diabetes.Dis Model Mech. 2016 Apr;9(4):365-76. doi: 10.1242/dmm.023887. Dis Model Mech. 2016. PMID: 27053133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An in vivo screen for neuronal genes involved in obesity identifies Diacylglycerol kinase as a regulator of insulin secretion.Mol Metab. 2019 Jan;19:13-23. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.10.006. Epub 2018 Oct 19. Mol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30389349 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atkinson NS, Robertson GA, Ganetzky B. A component of calcium-activated potassium channels encoded by the Drosophila slo locus. Science. 1991;253:551–555. - PubMed
-
- Schopperle WM, Holmqvist MH, Zhou Y, Wang J, Wang Z, et al. Slob, a novel protein that interacts with the Slowpoke calcium-dependent potassium channel. Neuron. 1998;20:565–573. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

