Targeting Mcl-1 for the therapy of cancer
- PMID: 21851287
- PMCID: PMC3205956
- DOI: 10.1517/13543784.2011.609167
Targeting Mcl-1 for the therapy of cancer
Abstract
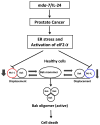
Introduction: Human cancers are genetically and epigenetically heterogeneous and have the capacity to commandeer a variety of cellular processes to aid in their survival, growth and resistance to therapy. One strategy is to overexpress proteins that suppress apoptosis, such as the Bcl-2 family protein Mcl-1. The Mcl-1 protein plays a pivotal role in protecting cells from apoptosis and is overexpressed in a variety of human cancers.
Areas covered: Targeting Mcl-1 for extinction in these cancers, using genetic and pharmacological approaches, represents a potentially effectual means of developing new efficacious cancer therapeutics. Here we review the multiple strategies that have been employed in targeting this fundamental protein, as well as the significant potential these targeting agents provide in not only suppressing cancer growth, but also in reversing resistance to conventional cancer treatments.
Expert opinion: We discuss the potential issues that arise in targeting Mcl-1 and other Bcl-2 anti-apoptotic proteins, as well problems with acquired resistance. The application of combinatorial approaches that involve inhibiting Mcl-1 and manipulation of additional signaling pathways to enhance therapeutic outcomes is also highlighted. The ability to specifically inhibit key genetic/epigenetic elements and biochemical pathways that maintain the tumor state represent a viable approach for developing rationally based, effective cancer therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state no conflict of interest and have received no payment in preparation of this manuscript.
Figures



References
-
- Mandelin A, Pope R. Myeloid cell leukemia-1 as a therapeutic target. Expert opinion on therapeutic targets. 2007;11(3):363. - PubMed
-
- Danial N. BCL-2 family proteins: Critical checkpoints of apoptotic cell death. Clinical cancer research. 2007;13(24):7254. - PubMed
-
- Reynolds JE, Yang T, Qian L, Jenkinson JD, Zhou P, Eastman A, et al. Mcl-1, a member of the bcl-2 family, delays apoptosis induced by c-myc overexpression in chinese hamster ovary cells. Cancer Res. 1994;54(24):6348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA259599/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2CA148431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 GM093857/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA142509/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA127641/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA100866/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA093738/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA097318/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA141703/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 CA148431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA104177/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK052825/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA150214/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA149668/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA130805/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
