Transcripts that associate with the RNA binding protein, DEAD-END (DND1), in embryonic stem (ES) cells
- PMID: 21851623
- PMCID: PMC3167746
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-12-37
Transcripts that associate with the RNA binding protein, DEAD-END (DND1), in embryonic stem (ES) cells
Abstract
Background: The RNA binding protein, DEAD END (DND1), is essential for maintaining viable germ cells in vertebrates. It is also a testicular germ cell tumor susceptibility factor in mice. DND1 has been shown to interact with the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of mRNAs such as P27 and LATS2. Binding of DND1 to the 3'-UTRs of these transcripts blocks the inhibitory function of microRNAs (miRNA) from these transcripts and in this way DND1 helps maintain P27 and LATS2 protein expression. We found that DND1 is also expressed in embryonic stem (ES) cells. Because ES cells share similar gene expression patterns as germ cells, we utilized ES cells to identify additional candidate mRNAs that associate with DND1.
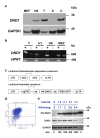
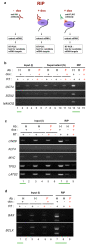
Results: ES cells are readily amenable to genetic modification and easier to culture in vitro compared to germ cells. Therefore, for the purpose of our study, we made a genetically modified, stable, human embryonic stem (hES) cell line that expresses hemagluttinin (HA)-tagged DND1 in a doxycycline (dox) regulatable manner. This line expresses modest levels of HA-DND1 and serves as a good system to study DND1 function in vitro. We used this stable cell line to identify the transcripts that physically interact with DND1. By performing ribonucleoprotein immunoprecipitation (RIP) followed by RT-PCR, we identified that transcripts encoding pluripotency factors (OCT4, SOX2, NANOG, LIN28), cell cycle regulators (TP53, LATS2) and apoptotic factors (BCLX, BAX) are specifically associated with the HA-DND1 ribonucleoprotein complex. Surprisingly, in many cases, bioinformatics analysis of the pulled-down transcripts did not reveal the presence of known DND1 interacting motifs.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that the inducible ES cell line system serves as a suitable in vitro system to identify the mRNA targets of DND1. The RIP-RT results hint at the broad spectrum of mRNA targets that interact with DND1 in ES cells. Based on what is known about DND1 function, our results suggest that DND1 may impose another level of translational regulation to modulate expression of critical factors in ES cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mouse apolipoprotein B editing complex 3 (APOBEC3) is expressed in germ cells and interacts with dead-end (DND1).PLoS One. 2008 May 28;3(5):e2315. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002315. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18509452 Free PMC article.
-
APOBEC3 inhibits DEAD-END function to regulate microRNA activity.BMC Mol Biol. 2013 Jul 26;14:16. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-14-16. BMC Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23890083 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of male germ cell cycle arrest and differentiation by DND1 is modulated by genetic background.Development. 2011 Jan;138(1):23-32. doi: 10.1242/dev.057000. Epub 2010 Nov 29. Development. 2011. PMID: 21115610 Free PMC article.
-
Embryonic stem cell microRNAs: defining factors in induced pluripotent (iPS) and cancer (CSC) stem cells?Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009 Sep;4(3):168-77. doi: 10.2174/157488809789057400. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19492978 Review.
-
The Role of DND1 in Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 22;13(15):3679. doi: 10.3390/cancers13153679. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34359581 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Parent-of-origin effects of A1CF and AGO2 on testicular germ-cell tumors, testicular abnormalities, and fertilization bias.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Sep 13;113(37):E5425-33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1604773113. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27582469 Free PMC article.
-
Reprogramming of germ cells into pluripotency.World J Stem Cells. 2016 Aug 26;8(8):251-9. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v8.i8.251. World J Stem Cells. 2016. PMID: 27621759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A transgenic DND1GFP fusion allele reports in vivo expression and RNA-binding targets in undifferentiated mouse germ cells†.Biol Reprod. 2021 Apr 1;104(4):861-874. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioaa233. Biol Reprod. 2021. PMID: 33394034 Free PMC article.
-
The ter mutation in the rat Dnd1 gene initiates gonadal teratomas and infertility in both genders.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e38001. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038001. Epub 2012 May 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22655094 Free PMC article.
-
Contrasting effects of Deadend1 (Dnd1) gain and loss of function mutations on allelic inheritance, testicular cancer, and intestinal polyposis.BMC Genet. 2013 Jun 17;14:54. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-14-54. BMC Genet. 2013. PMID: 23773267 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weidinger G, Stebler J, Slanchev K, Dumstrei K, Wise C, Lovell-Badge R, Thisse C, Thisse B, Raz E. dead end, a novel vertebrate germ plasm component, is required for zebrafish primordial germ cell migration and survival. Curr Biol. 2003;13(16):1429–1434. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(03)00537-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hayashi K, de Sousa Lopes SMC, Surani MA. Germ cell specification in mice. Science. 2007;314:394–396. - PubMed
-
- Noguchi T, Stevens LC. Primordial germ cell proliferation in fetal testes in mouse strains with high and low incidences of congenital testicular teratomas. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982;69(4):907–913. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

