Phytochrome signaling mechanisms and the control of plant development
- PMID: 21852137
- PMCID: PMC3205231
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2011.07.002
Phytochrome signaling mechanisms and the control of plant development
Abstract
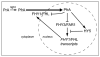
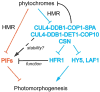
As they emerge from the ground, seedlings adopt a photosynthetic lifestyle, which is accompanied by dramatic changes in morphology and global alterations in gene expression that optimizes the plant body plan for light capture. Phytochromes are red and far-red photoreceptors that play a major role during photomorphogenesis, a complex developmental program that seedlings initiate when they first encounter light. The earliest phytochrome signaling events after excitation by red light include their rapid translocation from the cytoplasm to subnuclear bodies (photobodies) that contain other proteins involved in photomorphogenesis, including a number of transcription factors and E3 ligases. In the light, phytochromes and negatively acting transcriptional regulators that interact directly with phytochromes are destabilized, whereas positively acting transcriptional regulators are stabilized. Here, we discuss recent advances in our knowledge of the mechanisms linking phytochrome photoactivation in the cytoplasm and transcriptional regulation in the nucleus.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Chen M, et al. Light signal transduction in higher plants. Annu Rev Genet. 2004;38:87–117. - PubMed
-
- Jiao Y, et al. Light-regulated transcriptional networks in higher plants. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:217–230. - PubMed
-
- Tepperman JM, et al. phyA dominates in transduction of red-light signals to rapidly responding genes at the initiation of Arabidopsis seedling de-etiolation. Plant J. 2006;48:728–742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

