Immune intervention in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 21852151
- PMCID: PMC3177994
- DOI: 10.1016/j.smim.2011.07.003
Immune intervention in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
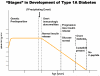
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is a chronic autoimmune disease that results in the specific immune destruction of insulin producing beta cells. Currently there is no cure for T1D and treatment for the disease consists of lifelong administration of insulin. Immunotherapies aimed at preventing beta cell destruction in T1D patients with residual c-peptide or in individuals developing T1D are being evaluated. Networks of researchers such as TrialNet and the Immune Tolerance Network in the U.S. and similar networks in Europe have been established to evaluate such immunotherapies. This review focuses on immune intervention for the prevention and amelioration of human T1D with a focus on potential immune suppressive, antigen specific and environmental therapies.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Maahs DM, Rewers M. Editorial: Mortality and renal disease in type 1 diabetes mellitus--progress made, more to be done. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91(10):3757–3759. - PubMed
-
- Steffes MW, Sibley S, Jackson M, Thomas W. Beta-cell function and the development of diabetes-related complications in the diabetes control and complications trial. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(3):832–836. - PubMed
-
- Harjutsalo V, Sjoberg L, Tuomilehto J. Time trends in the incidence of type 1 diabetes in Finnish children: a cohort study. Lancet. 2008;371(9626):1777–1782. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

