p53: guardian of ploidy
- PMID: 21852209
- PMCID: PMC3164924
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molonc.2011.07.007
p53: guardian of ploidy
Abstract
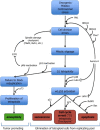
Aneuploidy, often preceded by tetraploidy, is one of the hallmarks of solid tumors. Indeed, both aneuploidy and tetraploidy are oncogenic occurrences that are sufficient to drive neoplastic transformation and cancer progression. True to form, the tumor suppressor p53 obstructs propagation of these dangerous chromosomal events by either instigating irreversible cell cycle arrest or apoptosis. The tumor suppressor Lats2, along with other tumor inhibitory proteins such as BRCA1/2 and BubR1, are central to p53-dependent elimination of tetraploid cells. Not surprisingly, these proteins are frequently inactivated or downregulated in tumors, synergizing with p53 inactivation to establish an atmosphere of "tolerance" for a non-diploid state.
Copyright © 2011 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ando, K. , Ozaki, T. , Yamamoto, H. , Furuya, K. , Hosoda, M. , Hayashi, S. , Fukuzawa, M. , Nakagawara, A. , 2004. Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) inhibits p53 function by physical interaction and phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem.. 279, 25549–25561. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

