Identification and functional and spectral characterization of a globin-coupled histidine kinase from Anaeromyxobacter sp. Fw109-5
- PMID: 21852234
- PMCID: PMC3195594
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.274811
Identification and functional and spectral characterization of a globin-coupled histidine kinase from Anaeromyxobacter sp. Fw109-5
Abstract
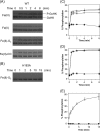
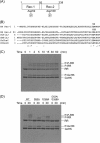
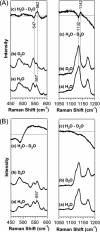
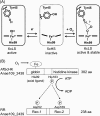
Two-component signal transduction systems regulate numerous important physiological functions in bacteria. In this study we have identified, cloned, overexpressed, and characterized a dimeric full-length heme-bound (heme:protein, 1:1 stoichiometry) globin-coupled histidine kinase (AfGcHK) from Anaeromyxobacter sp. strain Fw109-5 for the first time. The Fe(III), Fe(II)-O(2), and Fe(II)-CO complexes of the protein displayed autophosphorylation activity, whereas the Fe(II) complex had no significant activity. A H99A mutant lost heme binding ability, suggesting that this residue is the heme proximal ligand. Moreover, His-183 was proposed as the autophosphorylation site based on the finding that the H183A mutant protein was not phosphorylated. The phosphate group of autophosphorylated AfGcHK was transferred to Asp-52 and Asp-169 of a response regulator, as confirmed from site-directed mutagenesis experiments. Based on the amino acid sequences and crystal structures of other globin-coupled oxygen sensor enzymes, Tyr-45 was assumed to be the O(2) binding site at the heme distal side. The O(2) dissociation rate constant, 0.10 s(-1), was substantially increased up to 8.0 s(-1) upon Y45L mutation. The resonance Raman frequencies representing ν(Fe-O2) (559 cm(-1)) and ν(O-O) (1149 cm(-1)) of the Fe(II)-O(2) complex of Y45F mutant AfGcHK were distinct from those of the wild-type protein (ν(Fe-O2), 557 cm(-1); ν(O-O), 1141 cm(-1)), supporting the proposal that Tyr-45 is located at the distal side and forms hydrogen bonds with the oxygen molecule bound to the Fe(II) complex. Thus, we have successfully identified and characterized a novel heme-based globin-coupled oxygen sensor histidine kinase, AfGcHK, in this study.
Figures



References
-
- Inouye M., Dutta R. Eds. (2003) Histidine Kinases in Signal Transduction, Academic Press, Inc., San Diego, CA
-
- Krämer R., Jung K. Eds. (2010) Bacterial Signaling, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany
-
- Casino P., Rubio V., Marina A. (2010) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 20, 763–771 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

