Glutathione peroxidase-1 deficiency augments proinflammatory cytokine-induced redox signaling and human endothelial cell activation
- PMID: 21852236
- PMCID: PMC3195617
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.205708
Glutathione peroxidase-1 deficiency augments proinflammatory cytokine-induced redox signaling and human endothelial cell activation
Abstract
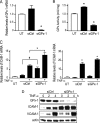
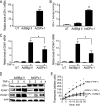
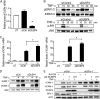
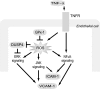
Glutathione peroxidase-1 (GPx-1) is a crucial antioxidant enzyme, the deficiency of which promotes atherogenesis. Accordingly, we examined the mechanisms by which GPx-1 deficiency enhances endothelial cell activation and inflammation. In human microvascular endothelial cells, we found that GPx-1 deficiency augments intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) expression by redox-dependent mechanisms that involve NFκB. Suppression of GPx-1 enhanced TNF-α-induced ROS production and ICAM-1 expression, whereas overexpression of GPx-1 attenuated these TNF-α-mediated responses. GPx-1 deficiency prolonged TNF-α-induced IκBα degradation and activation of ERK1/2 and JNK. JNK or NFκB inhibition attenuated TNF-α induction of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression in GPx-1-deficient and control cells, whereas ERK1/2 inhibition attenuated only VCAM-1 expression. To analyze further signaling pathways involved in GPx-1-mediated protection from TNF-α-induced ROS, we performed microarray analysis of human microvascular endothelial cells treated with TNF-α in the presence and absence of GPx-1. Among the genes whose expression changed significantly, dual specificity phosphatase 4 (DUSP4), encoding an antagonist of MAPK signaling, was down-regulated by GPx-1 suppression. Targeted DUSP4 knockdown enhanced TNF-α-mediated ERK1/2 pathway activation and resulted in increased adhesion molecule expression, indicating that GPx-1 deficiency may augment TNF-α-mediated events, in part, by regulating DUSP4.
Figures



References
-
- Raes M., Michiels C., Remacle J. (1987) Free Radic. Biol. Med. 3, 3–7 - PubMed
-
- Ursini F., Maiorino M., Brigelius-Flohé R., Aumann K. D., Roveri A., Schomburg D., Flohé L. (1995) Methods Enzymol. 252, 38–53 - PubMed
-
- Brigelius-Flohé R. (1999) Free Radic. Biol. Med. 27, 951–965 - PubMed
-
- de Haan J. B., Bladier C., Griffiths P., Kelner M., O'Shea R. D., Cheung N. S., Bronson R. T., Silvestro M. J., Wild S., Zheng S. S., Beart P. M., Hertzog P. J., Kola I. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273, 22528–22536 - PubMed
-
- Forgione M. A., Cap A., Liao R., Moldovan N. I., Eberhardt R. T., Lim C. C., Jones J., Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Loscalzo J. (2002) Circulation 106, 1154–1158 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

