Erk regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase flux through PDK4 modulates cell proliferation
- PMID: 21852536
- PMCID: PMC3165936
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.16771811
Erk regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase flux through PDK4 modulates cell proliferation
Abstract
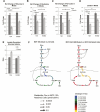
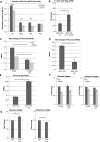
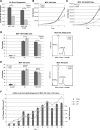
Loss of extracellular matrix (ECM) attachment leads to metabolic impairments that limit cellular energy production. Characterization of the metabolic alterations induced by ECM detachment revealed a dramatic decrease in uptake of glucose, glutamine, and pyruvate, and a consequent decrease in flux through glycolysis, the pentose phosphate pathway, and the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. However, flux through pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) is disproportionally decreased, concomitant with increased expression of the PDH inhibitory kinase, PDH kinase 4 (PDK4), and increased carbon secretion. Overexpression of ErbB2 maintains PDH flux by suppressing PDK4 expression in an Erk-dependent manner, and Erk signaling also regulates PDH flux in ECM-attached cells. Additionally, epidermal growth factor (EGF), a potent inducer of Erk, positively regulates PDH flux through decreased PDK4 expression. Furthermore, overexpression of PDK4 in ECM-detached cells suppresses the ErbB2-mediated rescue of ATP levels, and in attached cells, PDK4 overexpression decreases PDH flux, de novo lipogenesis, and cell proliferation. Mining of microarray data from human tumor data sets revealed that PDK4 mRNA is commonly down-regulated in tumors compared with their tissues of origin. These results identify a novel mechanism by which ECM attachment, growth factors, and oncogenes modulate the metabolic fate of glucose by controlling PDK4 expression and PDH flux to influence proliferation.
Figures





Comment in
-
Metabolic regulation by ERK.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Aug 23;12(9):546. doi: 10.1038/nrm3179. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21860387 No abstract available.
References
-
- Abbot EL, McCormack JG, Reynet C, Hassall DG, Buchan KW, Yeaman SJ 2005. Diverging regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isoform gene expression in cultured human muscle cells. FEBS J 272: 3004–3014 - PubMed
-
- Antoniewicz MR, Kelleher JK, Stephanopoulos G 2006. Determination of confidence intervals of metabolic fluxes estimated from stable isotope measurements. Metab Eng 8: 324–337 - PubMed
-
- Arnaud M, Crouin C, Deon C, Loyaux D, Bertoglio J 2004. Phosphorylation of Grb2-associated binder 2 on serine 623 by ERK MAPK regulates its association with the phosphatase SHP-2 and decreases STAT5 activation. J Immunol 173: 3962–3971 - PubMed
-
- Asada S, Daitoku H, Matsuzaki H, Saito T, Sudo T, Mukai H, Iwashita S, Kako K, Kishi T, Kasuya Y, et al. 2007. Mitogen-activated protein kinases, Erk and p38, phosphorylate and regulate Foxo1. Cell Signal 19: 519–527 - PubMed
-
- Bensaad K, Tsuruta A, Selak MA, Vidal MN, Nakano K, Bartrons R, Gottlieb E, Vousden KH 2006. TIGAR, a p53-inducible regulator of glycolysis and apoptosis. Cell 126: 107–120 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
