The regulation of valvular and vascular sclerosis by osteogenic morphogens
- PMID: 21852555
- PMCID: PMC3167074
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.234278
The regulation of valvular and vascular sclerosis by osteogenic morphogens
Abstract
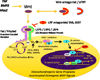
Vascular calcification increasingly afflicts our aging, dysmetabolic population. Once considered only a passive process of dead and dying cells, vascular calcification has now emerged as a highly regulated form of biomineralization organized by collagenous and elastin extracellular matrices. During skeletal bone formation, paracrine epithelial-mesenchymal and endothelial-mesenchymal interactions control osteochondrocytic differentiation of multipotent mesenchymal progenitor cells. These paracrine osteogenic signals, mediated by potent morphogens of the bone morphogenetic protein and wingless-type MMTV integration site family member (Wnt) superfamilies, are also active in the programming of arterial osteoprogenitor cells during vascular and valve calcification. Inflammatory cytokines, reactive oxygen species, and oxylipids-increased in the clinical settings of atherosclerosis, diabetes, and uremia that promote arteriosclerotic calcification-elicit the ectopic vascular activation of osteogenic morphogens. Specific extracellular and intracellular inhibitors of bone morphogenetic protein-Wnt signaling have been identified as contributing to the regulation of osteogenic mineralization during development and disease. These inhibitory pathways and their regulators afford the development of novel therapeutic strategies to prevent and treat valve and vascular sclerosis.
Figures


References
-
- Tanimura A, McGregor DH, Anderson HC. Calcification in atherosclerosis. I. Human studies. J Exp Pathol. 1986;2(4):261–273. - PubMed
-
- Tanimura A, McGregor DH, Anderson HC. Matrix vesicles in atherosclerotic calcification. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1983;172(2):173–177. - PubMed
-
- Urist MR, Strates BS. Bone formation in implants of partially and wholly demineralized bone matrix. Including observations on acetone-fixed intra and extracellular proteins. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1970;71:271–278. - PubMed
-
- Wozney JM, Rosen V, Celeste AJ, Mitsock LM, Whitters MJ, Kriz RW, Hewick RM, Wang EA. Novel regulators of bone formation: molecular clones and activities. Science. 1988;242(4885):1528–1534. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL081138/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 3R01HL085591S1/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL030568/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL069229/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL088651/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01HL085591/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL081397/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL088651/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL081138/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL085591/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL069229/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL081397/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL030568/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

