On safety, pharmacokinetics and dosage of bevacizumab in ROP treatment - a review
- PMID: 21854449
- PMCID: PMC3263420
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.2011.02445.x
On safety, pharmacokinetics and dosage of bevacizumab in ROP treatment - a review
Abstract
Off-label intravitreal use of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) antibody bevacizumab for retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) increases despite lack of studies on safety, pharmacokinetics and dosage in developing individuals. Systemic absorption has been considered negligible. A literature search was performed with emphasis on potential adverse systemic effects in developing individuals.
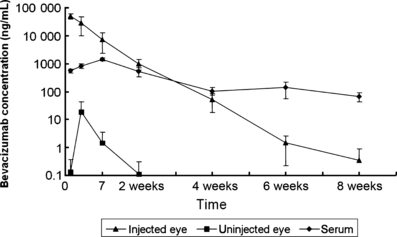
Conclusion: Intravitreal bevacizumab enters the general circulation, suppresses plasma VEGF levels and remains in the blood for more than 8 weeks in primates. Possible adverse effects on VEGF-dependent development must be considered.
© 2011 The Author(s)/Acta Paediatrica © 2011 Foundation Acta Paediatrica.
Figures
References
-
- Reynolds JD. Bevacizumab for retinopathy of prematurity. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:677–8. - PubMed
-
- Pulido JS. Monitoring systemic complications of intraocular medications. Can J Ophthalmol. 2010;45:215–7. - PubMed
-
- Micieli JA, Micieli A, Smith AF. Identifying systemic safety signals following intravitreal bevacizumab: systematic review of the literature and the Canadian Adverse Drug Reaction Database. Can J Ophthalmol. 2010;45:231–8. - PubMed
-
- Lin YS, Nguyen C, Mendoza JL, Escandon E, Fei D, Meng YG, et al. Preclinical pharmacokinetics, interspecies scaling, and tissue distribution of a humanized monoclonal antibody against vascular endothelial growth factor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999;288:371–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical