The resistance of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae to the biocide polyhexamethylene biguanide: involvement of cell wall integrity pathway and emerging role for YAP1
- PMID: 21854579
- PMCID: PMC3175164
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-12-38
The resistance of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae to the biocide polyhexamethylene biguanide: involvement of cell wall integrity pathway and emerging role for YAP1
Abstract
Background: Polyhexamethylene biguanide (PHMB) is an antiseptic polymer that is mainly used for cleaning hospitals and pools and combating Acantamoeba infection. Its fungicide activity was recently shown by its lethal effect on yeasts that contaminate the industrial ethanol process, and on the PE-2 strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, one of the main fermenting yeasts in Brazil. This pointed to the need to know the molecular mechanism that lay behind the cell resistance to this compound. In this study, we examined the factors involved in PHMB-cell interaction and the mechanisms that respond to the damage caused by this interaction. To achieve this, two research strategies were employed: the expression of some genes by RT-qPCR and the analysis of mutant strains.
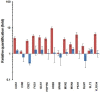
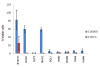
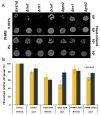
Results: Cell Wall integrity (CWI) genes were induced in the PHMB-resistant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain JP-1, although they are poorly expressed in the PHMB-sensitive Saccharomyces cerevisiae PE2 strain. This suggested that PHMB damages the glucan structure on the yeast cell wall. It was also confirmed by the observed sensitivity of the yeast deletion strains, Δslg1, Δrom2, Δmkk2, Δslt2, Δknr4, Δswi4 and Δswi4, which showed that the protein kinase C (PKC) regulatory mechanism is involved in the response and resistance to PHMB. The sensitivity of the Δhog1 mutant was also observed. Furthermore, the cytotoxicity assay and gene expression analysis showed that the part played by YAP1 and CTT1 genes in cell resistance to PHMB is unrelated to oxidative stress response. Thus, we suggested that Yap1p can play a role in cell wall maintenance by controlling the expression of the CWI genes.
Conclusion: The PHMB treatment of the yeast cells activates the PKC1/Slt2 (CWI) pathway. In addition, it is suggested that HOG1 and YAP1 can play a role in the regulation of CWI genes.
Figures

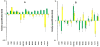
Similar articles
-
NCW2, a Gene Involved in the Tolerance to Polyhexamethylene Biguanide (PHMB), May Help in the Organisation of β-1,3-Glucan Structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cell Wall.Curr Microbiol. 2016 Sep;73(3):341-345. doi: 10.1007/s00284-016-1067-z. Epub 2016 May 31. Curr Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27246500
-
The effects of the Ncw2 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on the positioning of chitin in response to cell wall damage.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2020 Feb;113(2):265-277. doi: 10.1007/s10482-019-01335-y. Epub 2019 Oct 9. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2020. PMID: 31598818
-
The high osmotic response and cell wall integrity pathways cooperate to regulate transcriptional responses to zymolyase-induced cell wall stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2009 Apr 17;284(16):10901-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808693200. Epub 2009 Feb 20. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19234305 Free PMC article.
-
Control of Gene Expression via the Yeast CWI Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 4;23(3):1791. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031791. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Together we are strong--cell wall integrity sensors in yeasts.Yeast. 2010 Aug;27(8):531-40. doi: 10.1002/yea.1785. Yeast. 2010. PMID: 20641024 Review.
Cited by
-
UME6 Is Involved in the Suppression of Basal Transcription of ABC Transporters and Drug Resistance in the ρ+ Cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Microorganisms. 2022 Mar 10;10(3):601. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10030601. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35336175 Free PMC article.
-
NCW2, a Gene Involved in the Tolerance to Polyhexamethylene Biguanide (PHMB), May Help in the Organisation of β-1,3-Glucan Structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cell Wall.Curr Microbiol. 2016 Sep;73(3):341-345. doi: 10.1007/s00284-016-1067-z. Epub 2016 May 31. Curr Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27246500
-
Extreme Low Cytosolic pH Is a Signal for Cell Survival in Acid Stressed Yeast.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jun 16;11(6):656. doi: 10.3390/genes11060656. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32560106 Free PMC article.
-
RPD3 and UME6 are involved in the activation of PDR5 transcription and pleiotropic drug resistance in ρ0 cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.BMC Microbiol. 2021 Nov 9;21(1):311. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02373-1. BMC Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34753419 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of a Gentamicin-Resistant Variant Following Polyhexamethylene Biguanide (PHMB) Exposure in Escherichia coli Biofilms.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 May 10;10(5):553. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10050553. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34068600 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elsztein C, Scavuzzi de Menezes JA, Morais MA. Polyhexamethyl biguanide can eliminate contaminant yeasts from the fuel-ethanol fermentation process. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008;35(9):987–973. - PubMed
-
- Cazzaniga A, Serralta V, Davis S, Orr R, Eaglstein W, Mertz PM. The effect of an antimicrobial gauze dressing impregnated with 0.2-percent polyhexamethylene biguanide as a barrier to prevent Pseudomonas aeruginosa wound invasion. Wounds. 2002;14(5):169–176.
-
- Payne JD, Kudner DW. A durable antiodor finish for cotton textiles. Text Chem Color. 1996;28:28–30.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

