Cellular viability effects of fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibition on cerebellar neurons
- PMID: 21854612
- PMCID: PMC3171300
- DOI: 10.1186/1755-7682-4-28
Cellular viability effects of fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibition on cerebellar neurons
Abstract
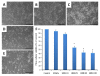
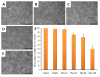
The endocannabinoid anandamide (ANA) participates in the control of cell death inducing the formation of apoptotic bodies and DNA fragmentation. The aim of this study was to evaluate whether the ANA degrading enzyme, the fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), would induce cellular death. Experiments were performed in cerebellar granule neurons cultured with the FAAH inhibitor, URB597 (25, 50 or 100 nM) as well as endogenous lipids such as oleoylethanolamide (OEA) or palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) and cellular viability was determined by MTT test. Neurons cultured with URB597 (25, 50 or 100 nM) displayed a decrease in cellular viability. In addition, if cultured with OEA (25 nM) or PEA (100 nM), cellular death was found. These results further suggest that URB597, OEA or PEA promote cellular death.
Figures

References
-
- Lambert DM, Di Marzo V. The palmitoylethanolamide and oleamide enigmas: are these two fatty acid amides cannabimimetic? Curr Med Chem. 1999;6(8):757–773. - PubMed
-
- Fu J, Gaetani S, Oveisi F, Lo Verme J, Serrano A, Rodriguez De Fonseca F, Rosengarth A, Luecke H, Di Giacomo B, Tarzia G. et al. Oleylethanolamide regulates feeding and body weight through activation of the nuclear receptor PPAR-alpha. Nature. 2003;425(6953):90–93. doi: 10.1038/nature01921. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
