Live-cell imaging of tumor proteolysis: impact of cellular and non-cellular microenvironment
- PMID: 21854877
- PMCID: PMC3232330
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2011.07.025
Live-cell imaging of tumor proteolysis: impact of cellular and non-cellular microenvironment
Abstract
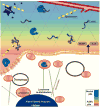
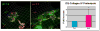
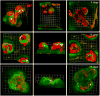
Our laboratory has had a longstanding interest in how the interactions between tumors and their microenvironment affect malignant progression. Recently, we have focused on defining the proteolytic pathways that function in the transition of breast cancer from the pre-invasive lesions of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) to invasive ductal carcinomas (IDCs). We use live-cell imaging to visualize, localize and quantify proteolysis as it occurs in real-time and thereby have established roles for lysosomal cysteine proteases both pericellularly and intracellularly in tumor proteolysis. To facilitate these studies, we have developed and optimized 3D organotypic co-culture models that recapitulate the in vivo interactions of mammary epithelial cells or tumor cells with stromal and inflammatory cells. Here we will discuss the background that led to our present studies as well as the techniques and models that we employ. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: Proteolysis 50 years after the discovery of lysosome.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
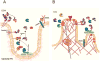

References
-
- Edwards DR, Hoyer-Hansen G, Blasi F, Sloane BF, editors. The Cancer Degradome--Proteases and Cancer Biology. Springer; New York: 2008.
-
- Cal S, Moncada-Pazos A, Lopez-Otin C. Expanding the complexity of the human degradome: polyserases and their tandem serine protease domains. Front Biosci. 2007;12:4661–4669. - PubMed
-
- Rawlings N, Barrett AJ. MEROPS: The peptidease database. [ http://merops.sanger.ac.uk/]
-
- Puente XS, Sanchez LM, Overall CM, Lopez-Otin C. Human and mouse proteases: a comparative genomic approach. Nat Rev Genet. 2003;4:544–558. - PubMed
-
- Vasiljeva O, Papazoglou A, Kruger A, Brodoefel H, Korovin M, Deussing J, Augustin N, Nielsen BS, Almholt K, Bogyo M, Peters C, Reinheckel T. Tumor cell-derived and macrophage-derived cathepsin B promotes progression and lung metastasis of mammary cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66:5242–5250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

