Structural linkage between ligand discrimination and receptor activation by type I interferons
- PMID: 21854986
- PMCID: PMC3166218
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.048
Structural linkage between ligand discrimination and receptor activation by type I interferons
Abstract
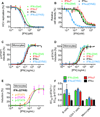
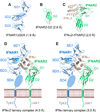
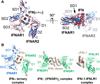
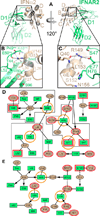
Type I Interferons (IFNs) are important cytokines for innate immunity against viruses and cancer. Sixteen human type I IFN variants signal through the same cell-surface receptors, IFNAR1 and IFNAR2, yet they can evoke markedly different physiological effects. The crystal structures of two human type I IFN ternary signaling complexes containing IFNα2 and IFNω reveal recognition modes and heterotrimeric architectures that are unique among the cytokine receptor superfamily but conserved between different type I IFNs. Receptor-ligand cross-reactivity is enabled by conserved receptor-ligand "anchor points" interspersed among ligand-specific interactions that "tune" the relative IFN-binding affinities, in an apparent extracellular "ligand proofreading" mechanism that modulates biological activity. Functional differences between IFNs are linked to their respective receptor recognition chemistries, in concert with a ligand-induced conformational change in IFNAR1, that collectively control signal initiation and complex stability, ultimately regulating differential STAT phosphorylation profiles, receptor internalization rates, and downstream gene expression patterns.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
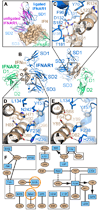

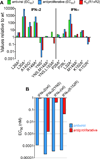
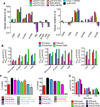
Comment in
-
Cytokines: Structuring the type I IFN response.Nat Rev Immunol. 2011 Sep 5;11(10):640. doi: 10.1038/nri3067. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21892203 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bleicher L, de Moura PR, Watanabe L, Colau D, Dumoutier L, Renauld JC, Polikarpov I. Crystal structure of the IL-22/IL-22R1 complex and its implications for the IL-22 signaling mechanism. FEBS Lett. 2008;582:2985–2992. - PubMed
-
- Bogdan C. The function of type I interferons in antimicrobial immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 2000;12:419–424. - PubMed
-
- Cajean-Feroldi C, Nosal F, Nardeux PC, Gallet X, Guymarho J, Baychelier F, Sempe P, Tovey MG, Escary JL, Eid P. Identification of residues of the IFNAR1 chain of the type I human interferon receptor critical for ligand binding and biological activity. Biochemistry. 2004;43:12498–12512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

