Glutamatergic plasticity in medial prefrontal cortex and ventral tegmental area following extended-access cocaine self-administration
- PMID: 21855055
- PMCID: PMC4000163
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.06.041
Glutamatergic plasticity in medial prefrontal cortex and ventral tegmental area following extended-access cocaine self-administration
Abstract
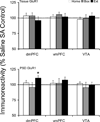
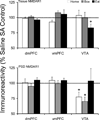
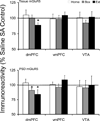
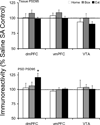
Glutamate signaling in prefrontal cortex and ventral tegmental area plays an important role in the molecular and behavioral plasticity associated with addiction to drugs of abuse. The current study investigated the expression and postsynaptic density redistribution of glutamate receptors and synaptic scaffolding proteins in dorsomedial and ventromedial prefrontal cortex and ventral tegmental area after cocaine self-administration. After 14 days of extended-access (6h/day) cocaine self-administration, rats were exposed to one of three withdrawal regimen for 10 days. Animals either stayed in home cages (Home), returned to self-administration boxes with the levers withdrawn (Box), or underwent extinction training (Extinction). Extinction training was associated with significant glutamatergic plasticity. In dorsomedial prefrontal cortex of the Extinction group, there was an increase in postsynaptic density GluR1, PSD95, and actin proteins; while postsynaptic density mGluR5 protein decreased and there was no change in NMDAR1, Homer1b/c, or PICK1 proteins. These changes were not observed in ventromedial prefrontal cortex or ventral tegmental area. In ventral tegmental area, Extinction training reversed the decreased postsynaptic density NMDAR1 protein in the Home and Box withdrawal groups. These data suggest that extinction of drug seeking is associated with selective glutamatergic plasticity in prefrontal cortex and ventral tegmental area that include modulation of receptor trafficking to postsynaptic density.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Behavioral sensitization to cocaine is associated with increased glutamate receptor trafficking to the postsynaptic density after extended withdrawal period.Neuroscience. 2009 Mar 3;159(1):414-26. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.10.027. Epub 2008 Nov 1. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19105975
-
Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors in the medial prefrontal cortex: role in mesocorticolimbic glutamate release in cocaine sensitization.Synapse. 2013 Dec;67(12):887-96. doi: 10.1002/syn.21699. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Synapse. 2013. PMID: 23913407
-
Neuroadaptations in the cellular and postsynaptic group 1 metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5 and Homer proteins following extinction of cocaine self-administration.Neurosci Lett. 2009 Mar 13;452(2):167-71. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.12.028. Epub 2008 Dec 24. Neurosci Lett. 2009. PMID: 19118598 Free PMC article.
-
Ventral tegmental glutamate: a role in stress-, cue-, and cocaine-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking.Neuropharmacology. 2009;56 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):174-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.06.008. Epub 2008 Jun 13. Neuropharmacology. 2009. PMID: 18598707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug-Evoked Synaptic Plasticity of Excitatory Transmission in the Ventral Tegmental Area.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2021 Apr 1;11(4):a039701. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a039701. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2021. PMID: 32341062 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Control Over Stress Accelerates Extinction of Drug Seeking Via Prefrontal Cortical Activation.Neurobiol Stress. 2015;2:20-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2015.03.002. Neurobiol Stress. 2015. PMID: 25954765 Free PMC article.
-
The Divergent Effects of CDPPB and Cannabidiol on Fear Extinction and Anxiety in a Predator Scent Stress Model of PTSD in Rats.Front Behav Neurosci. 2019 May 10;13:91. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00091. eCollection 2019. Front Behav Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31133832 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms underlying the efficacy of exercise as an intervention for cocaine relapse: a focus on mGlu5 in the dorsal medial prefrontal cortex.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Jul;236(7):2155-2171. doi: 10.1007/s00213-019-05208-0. Epub 2019 Jun 3. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 31161451 Free PMC article.
-
Contributions of prolonged contingent and non-contingent cocaine exposure to escalation of cocaine intake and glutamatergic gene expression.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018 May;235(5):1347-1359. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4798-z. Epub 2017 Dec 12. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018. PMID: 29234834 Free PMC article.
-
Nerve injury-induced changes in Homer/glutamate receptor signaling contribute to the development and maintenance of neuropathic pain.Pain. 2013 Oct;154(10):1932-1945. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2013.03.035. Epub 2013 Apr 2. Pain. 2013. PMID: 23685007 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson SM, Famous KR, Sadri-Vakili G, Kumaresan V, Schmidt HD, Bass CE, Terwilliger EF, Cha JH, Pierce RC. CaMKII: a biochemical bridge linking accumbens dopamine and glutamate systems in cocaine seeking. Nat Neurosci. 2008;11:344–353. - PubMed
-
- Bäckström P, Hyytiä P. Ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonism attenuates cue-induced cocaine seeking. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006;31:778–786. - PubMed
-
- Beckstead RM. An autoradiographic examination of corticocortical and subcortical projections of the mediodorsal-projection (prefrontal) cortex in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1979;184:43–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

