3xTgAD mice exhibit altered behavior and elevated Aβ after chronic mild social stress
- PMID: 21855175
- PMCID: PMC4074356
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.07.005
3xTgAD mice exhibit altered behavior and elevated Aβ after chronic mild social stress
Abstract
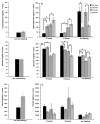
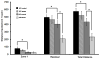
Chronic stress may be a risk factor for developing Alzheimer's disease (AD), but most studies of the effects of stress in models of AD utilize acute adverse stressors of questionable clinical relevance. The goal of this work was to determine how chronic psychosocial stress affects behavioral and pathological outcomes in an animal model of AD, and to elucidate underlying mechanisms. A triple-transgenic mouse model of AD (3xTgAD mice) and nontransgenic control mice were used to test for an affect of chronic mild social stress on blood glucose, plasma glucocorticoids, plasma insulin, anxiety, and hippocampal amyloid β-particle (Aβ), phosphorylated tau (ptau), and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels. Despite the fact that both control and 3xTgAD mice experienced rises in corticosterone during episodes of mild social stress, at the end of the 6-week stress period 3xTgAD mice displayed increased anxiety, elevated levels of Aβ oligomers and intraneuronal Aβ, and decreased brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels, whereas control mice did not. Findings suggest 3xTgAD mice are more vulnerable than control mice to chronic psychosocial stress, and that such chronic stress exacerbates Aβ accumulation and impairs neurotrophic signaling.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chronic mild sleep restriction accentuates contextual memory impairments, and accumulations of cortical Aβ and pTau in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Brain Res. 2013 Sep 5;1529:200-8. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.07.010. Epub 2013 Jul 13. Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23856323 Free PMC article.
-
Intraneuronal beta-amyloid accumulation in the amygdala enhances fear and anxiety in Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice.Biol Psychiatry. 2010 Mar 15;67(6):513-21. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.06.015. Epub 2009 Aug 7. Biol Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 19664757
-
The KATP channel activator diazoxide ameliorates amyloid-β and tau pathologies and improves memory in the 3xTgAD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;22(2):443-57. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-101017. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010. PMID: 20847430 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Role of Aggregated Proteomes in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020;21(12):1164-1173. doi: 10.2174/1389203721666200921152246. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020. PMID: 32957903 Review.
-
Effects of CX3CR1 and Fractalkine Chemokines in Amyloid Beta Clearance and p-Tau Accumulation in Alzheimer's Disease (AD) Rodent Models: Is Fractalkine a Systemic Biomarker for AD?Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016;13(4):403-12. doi: 10.2174/1567205013666151116125714. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016. PMID: 26567742 Review.
Cited by
-
Sleep, circadian rhythms, and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease.Exp Mol Med. 2015 Mar 13;47(3):e148. doi: 10.1038/emm.2014.121. Exp Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25766617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Actions of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Glucocorticoid Stress in Neurogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 2;18(11):2312. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112312. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29099059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglia, Lifestyle Stress, and Neurodegeneration.Immunity. 2020 Feb 18;52(2):222-240. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.12.003. Epub 2020 Jan 7. Immunity. 2020. PMID: 31924476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Severe Cognitive Dysfunction and Occupational Extremely Low Frequency Magnetic Field Exposure among Elderly Mexican Americans.Br J Med Med Res. 2014 Apr 16;4(8):1641-1662. doi: 10.9734/BJMMR/2014/7317. Br J Med Med Res. 2014. PMID: 24839595 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive Effects of Simulated Galactic Cosmic Radiation Are Mediated by ApoE Status, Sex, and Environment in APP Knock-In Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 29;25(17):9379. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179379. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273325 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akram A, Christoffel D, Rocher AB, Bouras C, Kövari E, Perl DP, Morrison JH, Herrmann FR, Haroutunian V, Giannakopoulos P, Hof PR. Stereologic estimates of total spinophilin-immunoreactive spine number in area 9 and the CA1 field: relationship with the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2008;29:1296–1307. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alfarez DN, De Simoni A, Velzing EH, Bracey E, Joëls M, Edwards FA, Krugers HJ. Corticosterone reduces dendritic complexity in developing hippocampal CA1 neurons. Hippocampus. 2009;19:828–836. - PubMed
-
- Alzoubi KH, Abdul-Razzak KK, Khabour OF, Al-Tuweiq GM, Alzubi MA, Alkadhi KA. Adverse effect of combination of chronic psychosocial stress and high fat diet on hippocampus-dependent memory in rats. Behav Brain Res. 2009;204:117–123. - PubMed
-
- Antonawich FJ, Miller G, Rigsby DC, Davis JN. Regulation of ischemic cell death by glucocorticoids and adrenocorticotropic hormone. Neuroscience. 1999;88:319–325. - PubMed
-
- Arabadzisz D, Diaz-Heijtz R, Knuesel I, Weber E, Pilloud S, Dettling AC, Feldon J, Law AJ, Harrison PJ, Pryce CR. Primate early life stress leads to long-term mild hippocampal decreases in corticosteroid receptor expression. Biol Psychiat. 2010;67:1106–1109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

