A high-throughput screening assay of ascorbate in brain samples
- PMID: 21855575
- PMCID: PMC3276367
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2011.08.001
A high-throughput screening assay of ascorbate in brain samples
Abstract
Ascorbate is a vital reductant/free radical scavenger in the CNS, whose content defines - to a large extent - the redox status and the antioxidant reserves. Quick, reliable and specific methods for its measurement in brain samples are highly desirable. We have developed a new high-throughput screening assay for measurements of ascorbate using a fluorescence plate-reader. This assay is based on a direct reaction of ascorbate with a nitroxide radical conjugated with a fluorogenic acridine moiety, 4-((9-acridinecarbonyl)-amino)-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl radical (AC-TEMPO), yielding fluorescent hydroxylamine product (AC-TEMPO-H). The reaction was monitored over time using fluorescence and electron spin resonance techniques. The appearance of fluorescent AC-TEMPO-H was linear within the range of 3.75-75μM AscH(-) in the sample (0.5-10μM AscH(-) in the well). Assay was validated with high performance liquid chromatography method. The concentration of ascorbate in murine tissue samples, including brain samples after traumatic brain injury and hemorrhagic shock, was measured.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
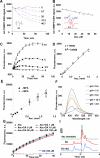
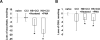
References
-
- User Verification of Performance for Precision and Trueness; Approved Guideline. 2006. p. 64. Chairholder: R. Neill Carey, PhD, FACB.
-
- Imprecision Spreadsheet provides example calculations for estimating imprecision that conform to CLSI documents EP05-A2 (Precision Performance of Clinical Chemistry Devices) and EP15-A2 (User Verification of Performance for Precision and Trueness)
-
- Ates O, Cayli S, Altinoz E, Gurses I, Yucel N, Sener M, Kocak A, Yologlu S. Neuroprotection by resveratrol against traumatic brain injury in rats. Mol Cell Biochem. 2007;294:137–44. - PubMed
-
- Bayir H, Kagan VE, Tyurina YY, Tyurin V, Ruppel RA, Adelson PD, Graham SH, Janesko K, Clark RS, Kochanek PM. Assessment of antioxidant reserves and oxidative stress in cerebrospinal fluid after severe traumatic brain injury in infants and children. Pediatr Res. 2002;51:571–8. - PubMed
-
- Behringer W, Safar P, Kentner R, Wu X, Kagan VE, Radovsky A, Clark RS, Kochanek PM, Subramanian M, Tyurin VA, Tyurina YY, Tisherman SA. Antioxidant Tempol enhances hypothermic cerebral preservation during prolonged cardiac arrest in dogs. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2002;22:105–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL070755/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- NS061817/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 OH008282/OH/NIOSH CDC HHS/United States
- R37 NS061817/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HD057587/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS030318/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HL70755/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI068021/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HD057587/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- NS30318/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS030318/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- OH008282/OH/NIOSH CDC HHS/United States
- R01 NS061817/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

