Knockdown of MADD and c-FLIP overcomes resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells
- PMID: 21855847
- PMCID: PMC3217125
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajog.2011.05.035
Knockdown of MADD and c-FLIP overcomes resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells
Abstract
Objective: The clinical utility of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) in the treatment of established human malignancies is limited by the development of resistance to TRAIL. We hypothesized that knockdown of map-kinase activating death domain containing protein (MADD), a TRAIL-resistance factor, may overcome TRAIL resistance in ovarian cancer cells.
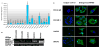
Study design: MADD expression in resected ovarian cancer specimens and cell lines was quantified with the use of polymerase chain reaction. Sensitivity of ovarian cancer cell lines to TRAIL, with or without MADD knockdown, was assessed.
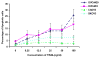
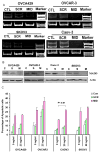
Results: MADD is expressed at relatively higher levels in human malignant ovarian cancer tissues and cell lines, compared with normal ovarian tissues. The cell lines OVCA429 and OVCAR3 were susceptible, and cell lines CAOV-3 and SKOV-3 were resistant to TRAIL. MADD knockdown in CAOV-3 cells, but not in SKOV-3 cells, conferred TRAIL sensitivity. Knockdown of cellular Fas-associated death domain-like interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme-inhibitory protein (c-FLIP) in SKOV-3 cells increased spontaneous and TRAIL-induced apoptosis, which was further increased on MADD knockdown.
Conclusion: MADD/c-FLIP(L) knockdown can render TRAIL-resistant ovarian cancer cells susceptible to TRAIL.
Copyright © 2011 Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURE: None of the authors have a conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Down-modulation of expression, or dephosphorylation, of IG20/MADD in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-resistant thyroid cancer cells makes them susceptible to treatment with this ligand.Thyroid. 2013 Jan;23(1):70-8. doi: 10.1089/thy.2012.0155. Thyroid. 2013. PMID: 22998497 Free PMC article.
-
Akt-phosphorylated mitogen-activated kinase-activating death domain protein (MADD) inhibits TRAIL-induced apoptosis by blocking Fas-associated death domain (FADD) association with death receptor 4.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 16;285(29):22713-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.105692. Epub 2010 May 18. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20484047 Free PMC article.
-
MADD/DENN splice variant of the IG20 gene is a negative regulator of caspase-8 activation. Knockdown enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis of cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2007 Apr 20;282(16):11715-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M701085200. Epub 2007 Feb 21. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17314102
-
Down-regulation of intracellular anti-apoptotic proteins, particularly c-FLIP by therapeutic agents; the novel view to overcome resistance to TRAIL.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Oct;233(10):6470-6485. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26585. Epub 2018 May 9. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29741767 Review.
-
Mechanisms of resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in cancer.Cancer Gene Ther. 2005 Mar;12(3):228-37. doi: 10.1038/sj.cgt.7700792. Cancer Gene Ther. 2005. PMID: 15550937 Review.
Cited by
-
The pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepine, PBOX-15, enhances TRAIL‑induced apoptosis by upregulation of DR5 and downregulation of core cell survival proteins in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cells.Int J Oncol. 2016 Jul;49(1):74-88. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3518. Epub 2016 May 12. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27176505 Free PMC article.
-
Down-modulation of expression, or dephosphorylation, of IG20/MADD in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-resistant thyroid cancer cells makes them susceptible to treatment with this ligand.Thyroid. 2013 Jan;23(1):70-8. doi: 10.1089/thy.2012.0155. Thyroid. 2013. PMID: 22998497 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into the role of p62 in the cisplatin resistant mechanisms of ovarian cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Apr 16;20:128. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01196-w. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 32322174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the metabolic pathway of human colon cancer overcomes resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis.Cell Death Discov. 2016 Sep 12;2:16067. doi: 10.1038/cddiscovery.2016.67. eCollection 2016. Cell Death Discov. 2016. PMID: 27648301 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative splicing as a biomarker and potential target for drug discovery.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015 Oct;36(10):1212-8. doi: 10.1038/aps.2015.43. Epub 2015 Jun 15. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015. PMID: 26073330 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. - PubMed
-
- Qazi F, McGuire WP. The treatment of epithelial ovarian cancer. CA Cancer J Clin. 1995;45:88–101. - PubMed
-
- Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, et al. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity. 1995;3:673–82. - PubMed
-
- Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, et al. Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med. 1999;5:157–63. - PubMed
-
- Okada H, Mak TW. Pathways of apoptotic and non-apoptotic death in tumour cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:592–603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

