Inhibition of aldose reductase prevents endotoxin-induced inflammation by regulating the arachidonic acid pathway in murine macrophages
- PMID: 21856412
- PMCID: PMC3188329
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.07.024
Inhibition of aldose reductase prevents endotoxin-induced inflammation by regulating the arachidonic acid pathway in murine macrophages
Abstract
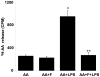
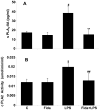
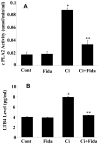
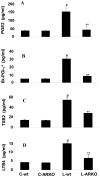
The bacterial endotoxin lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is known to induce release of arachidonic acid (AA) and its metabolic products, which play important roles in the inflammatory process. We have shown earlier that LPS-induced signals in macrophages are mediated by aldose reductase (AR). Here we have investigated the role of AR in LPS-induced release of AA metabolites and their modulation using a potent pharmacological inhibitor, fidarestat, and AR siRNA ablation in RAW264.7 macrophages and AR-knockout mouse peritoneal macrophages and heart tissue. Inhibition or genetic ablation of AR prevented the LPS-induced synthesis and release of AA metabolites such as PGE2, TXB, PGI2, and LTBs in macrophages. LPS-induced activation of cPLA2 was also prevented by AR inhibition. Similarly, AR inhibition also prevented the calcium ionophore A23187-induced cPLA2 and LTB4 in macrophages. Further, AR inhibition by fidarestat prevented the expression of AA-metabolizing enzymes such as COX-2 and LOX-5 in RAW264.7 cells and AR-knockout mouse-derived peritoneal macrophages. LPS-induced expression of AA-metabolizing enzymes and their catalyzed metabolic products was significantly lower in peritoneal macrophages and heart tissue from AR-knockout mice. LPS-induced activation of redox-sensitive signaling intermediates such as MAPKs, transcription factor NF-κB, and EGR-1, a transcriptional regulator of mPGES-1, which in collaboration with COX-2 leads to the production of PGE2, was also significantly prevented by AR inhibition. Taken together, our results indicate that AR mediates LPS-induced inflammation by regulating the AA-metabolic pathway and thus provide a novel role for AR inhibition in preventing inflammatory complications such as sepsis.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Aldose reductase mediates the lipopolysaccharide-induced release of inflammatory mediators in RAW264.7 murine macrophages.J Biol Chem. 2006 Nov 3;281(44):33019-29. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M603819200. Epub 2006 Sep 6. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16956889
-
Aldose reductase mediates endotoxin-induced production of nitric oxide and cytotoxicity in murine macrophages.Free Radic Biol Med. 2007 Apr 15;42(8):1290-302. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.01.033. Epub 2007 Jan 24. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007. PMID: 17382209 Free PMC article.
-
Aldose reductase inhibition prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced glucose uptake and glucose transporter 3 expression in RAW264.7 macrophages.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010 Jun;42(6):1039-45. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2010.03.014. Epub 2010 Mar 27. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20348015 Free PMC article.
-
A potential therapeutic role for aldose reductase inhibitors in the treatment of endotoxin-related inflammatory diseases.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2012 Mar;21(3):329-39. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2012.656198. Epub 2012 Jan 28. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22283786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aldose reductase inhibition suppresses oxidative stress-induced inflammatory disorders.Chem Biol Interact. 2011 May 30;191(1-3):330-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2011.02.023. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Chem Biol Interact. 2011. PMID: 21354119 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroprotective effect of aldose reductase knockout in a mouse model of spinal cord injury involves NF-κB pathway.Exp Brain Res. 2022 Mar;240(3):853-859. doi: 10.1007/s00221-021-06223-4. Epub 2022 Jan 23. Exp Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 35066597
-
Angong Niuhuang Pill ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice partly by restoring gut microbiota dysbiosis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 15;13:1001422. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1001422. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36188565 Free PMC article.
-
Arachidonic acid metabolism in health and disease.MedComm (2020). 2023 Sep 20;4(5):e363. doi: 10.1002/mco2.363. eCollection 2023 Oct. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37746665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aldose reductase participates in the downregulation of T cell functions due to suppressor macrophages.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 12;6:21093. doi: 10.1038/srep21093. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26868163 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of leukotriene B4 receptor 1 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction: role of AMPK-regulated mitochondrial function.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 14;7:44352. doi: 10.1038/srep44352. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28290498 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mayer RJ, Marshall LA. New insights on mammalian phospholipase A2(s); comparison of arachidonoyl-selective and -nonselective enzymes. FASEB J. 1993;7:339–348. - PubMed
-
- Dermott JM, Reddy MR, Onesime D, Reddy EP, Dhanasekaran N. Oncogenic mutant of Galpha12 stimulates cell proliferation through cycloxygenase-2 signaling pathway. Oncogene. 1999;18:7185–7189. - PubMed
-
- Leslie CC. Properties and regulation of cytosolic phospholipase A2. J BiolChem. 1997;272:16709–16712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

